How to fix missing think tag for Kimi K2.5
This guide demonstrates how to resolve the "Kimi K2.5 is not thinking" issue. It shows the underlying problem, the opening <think> tag is missing from the generated responses, and provides a fix by modifying the http API request with Ozeki AI Gateway.
Understanding the problem
This issue has been reported across multiple platforms and AI clients. Users running Kimi K2.5 with sglang or accessing it through various AI gateways encounter the same problem: the model returns reasoning content with only a closing </think> tag, breaking compatibility with clients like Open WebUI, Cline, KiloCode and Claude code that expect properly formatted reasoning blocks.
Community Discussion:
For more context about the issue, you can read the following Reddit thread:
kimi_k25_using_ktkernel_sglang
Using Open WebUI to demonstrate the problem
Watch the following video on how to configure Open WebUI for Kimi K2.5 and see how does it behave by not displaying the "Thinking" properly.
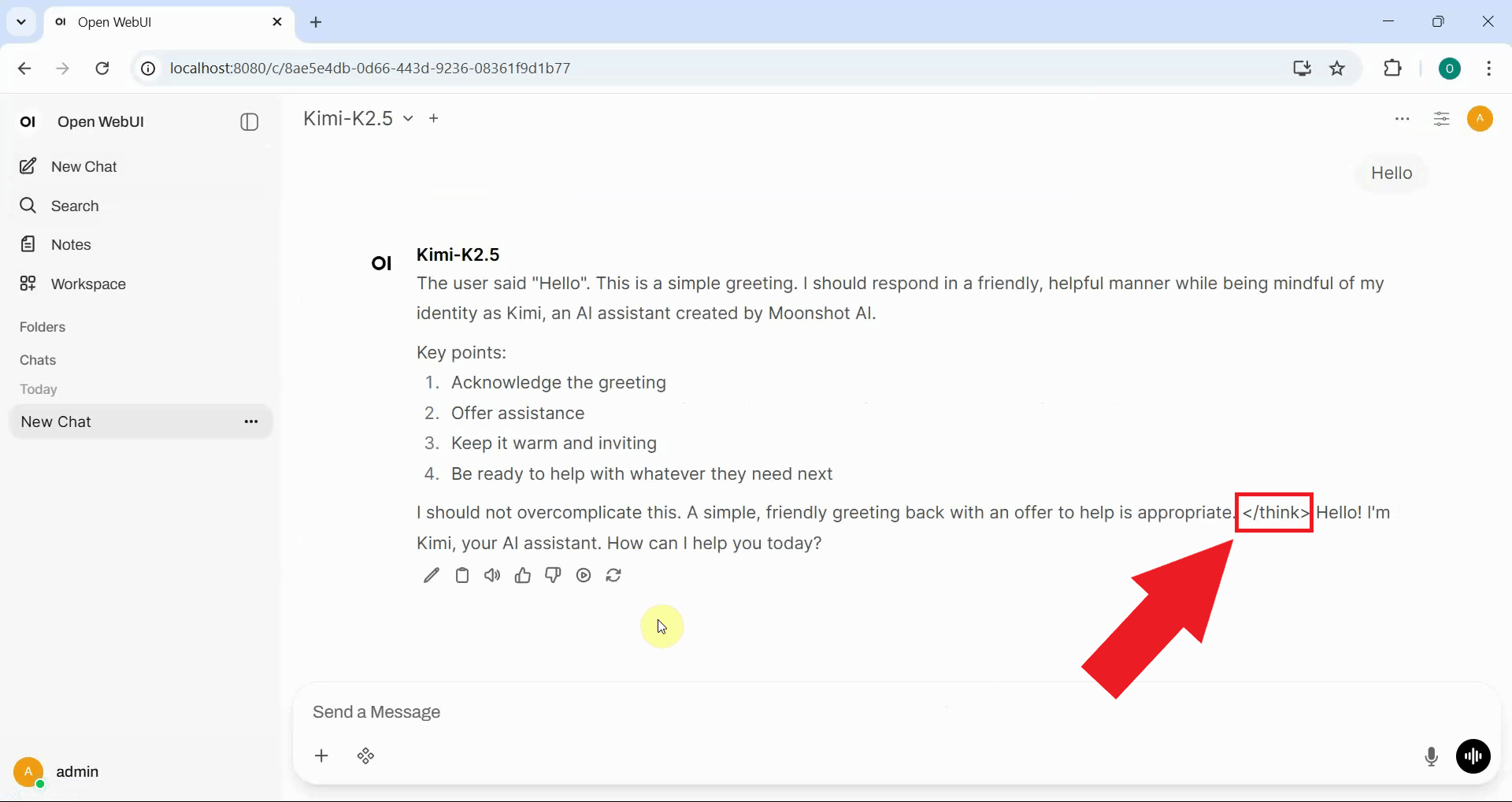
No start <think> tag, but there is a closing </think> tag in response
If you examine the model's response, and you'll notice that the reasoning content appears directly in the main message without proper separation, followed by a </think> closing tag and then the actual answer. The missing opening <think> tag prevents Open WebUI from correctly parsing the reasoning section into a separate collapsible area (Figure 1).
Solution: Route Kimi K2.5 through Ozeki AI Gateway and modify the requests
The best way to solve this problem is to route the requests through Ozeki AI Gateway and to modify the request by adding the following extra parameter to the request:
chat_template_kwargs": {"enable_thinking": true, "thinking": true}
This solution was suggested in the mentioned reddit thread.
Steps to follow
We assume Ozeki AI Gateway is already installed on your system. You can install it on Linux or on Windows.
- Add new provider in Ozeki AI Gateway
- Create a new user
- Generate an API key for the user
- Create a new route
- Add new connection for Ozeki AI Gateway in Open WebUI
- Send test prompt from Open WebUI
- Check logs in Ozeki AI Gateway
- Add new route request modifier
- Create custom modifier
- Send test prompt and verify response
- Check logs in Ozeki AI Gateway
Configure Ozeki AI Gateway
The following video shows how to configure Ozeki AI Gateway and route AI requests through it. The video demonstrates setting up a provider, creating a user with API access, configuring a route, and connecting Open WebUI to the gateway. You'll observe that the missing think tag issue persists when requests pass through the gateway without modifications.
Step 1 - Add new provider in Ozeki AI Gateway
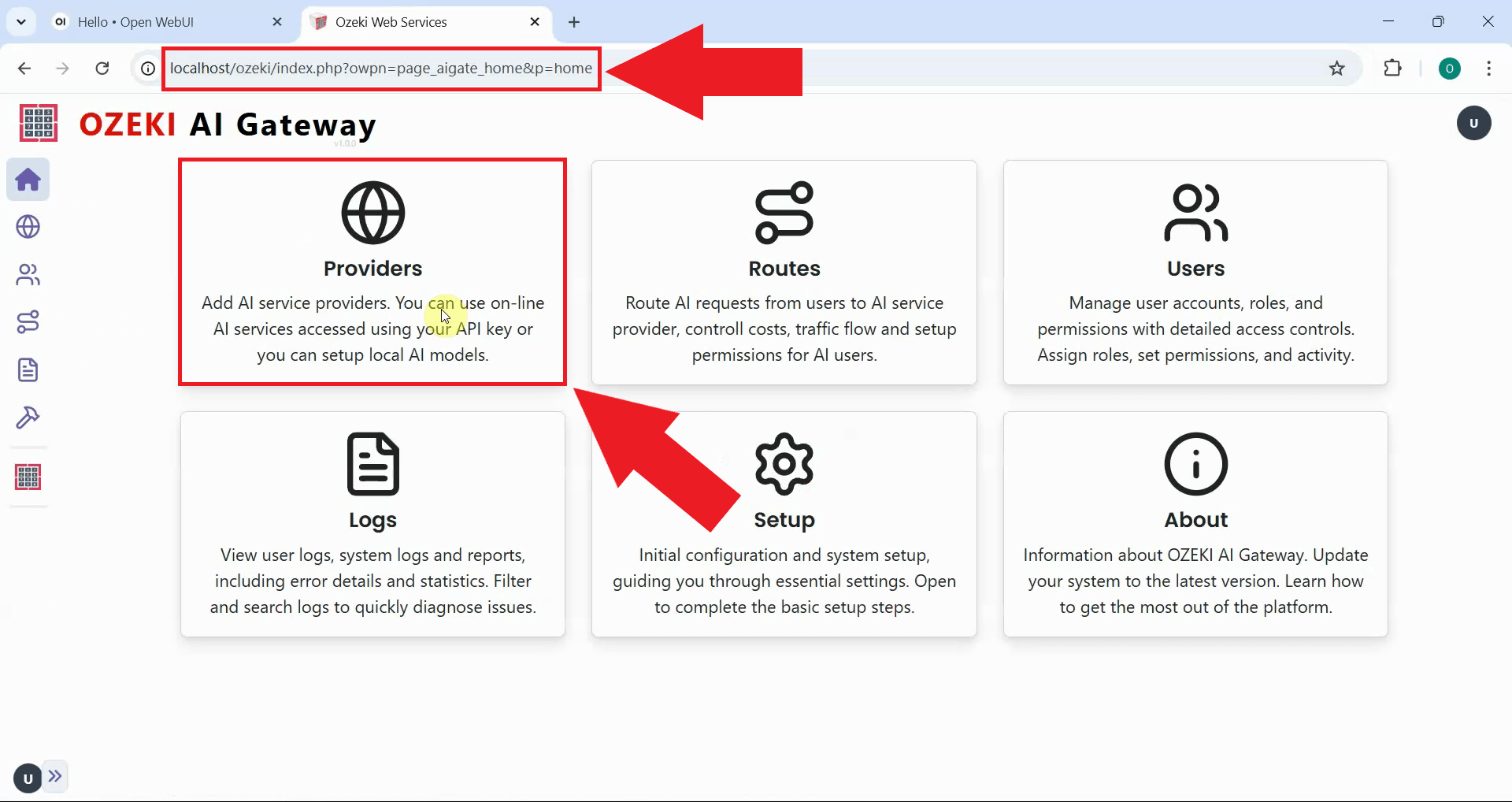
Launch the Ozeki AI Gateway web interface in your browser and navigate to the Providers page from the main menu. The Providers page displays all configured AI model connections and allows you to add new providers (Figure 2).
If you haven't installed Ozeki AI Gateway yet, follow our How to Install Ozeki AI Gateway on Linux to complete the initial setup.
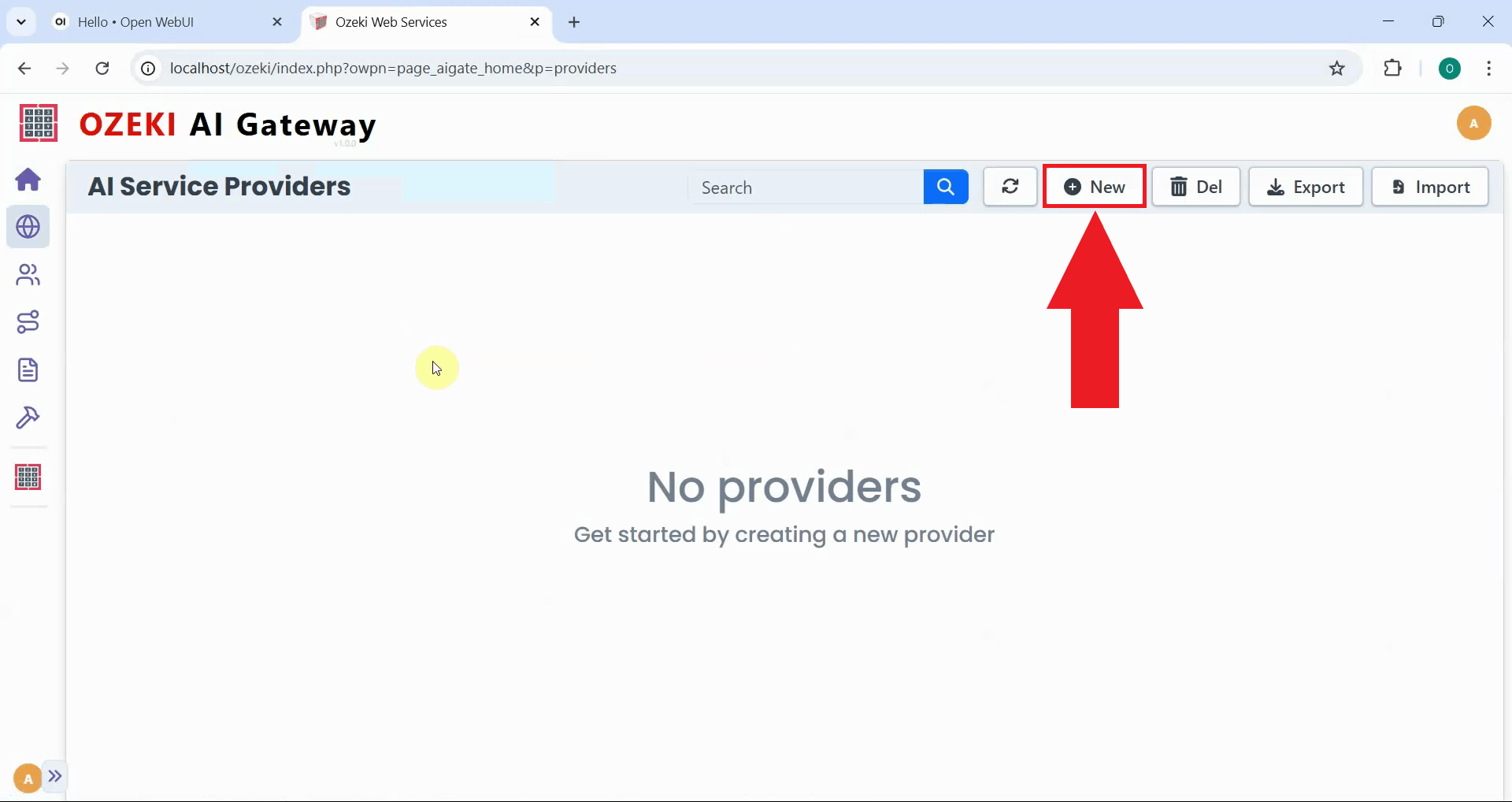
Click the "New" button on the Providers page to begin creating a provider configuration. This opens a form where you'll specify the connection details for your Kimi K2.5 server (Figure 3).
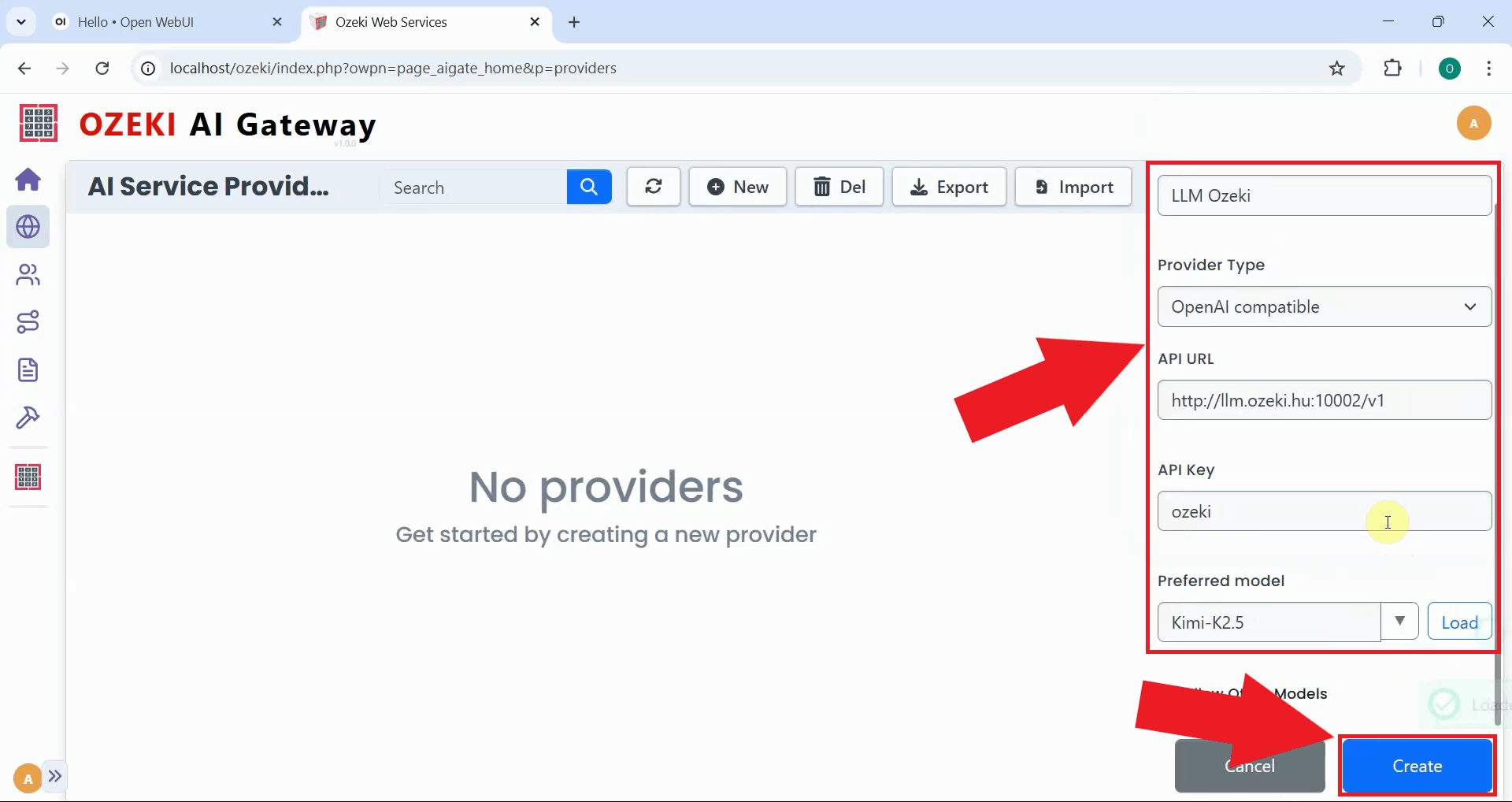
Fill in the provider form with your Kimi K2.5 server information including the API URL and model name. Select "OpenAI compatible" as the provider type since Kimi K2.5 uses the OpenAI API format. Click "Create" to save the provider configuration and make it available for routing (Figure 4).
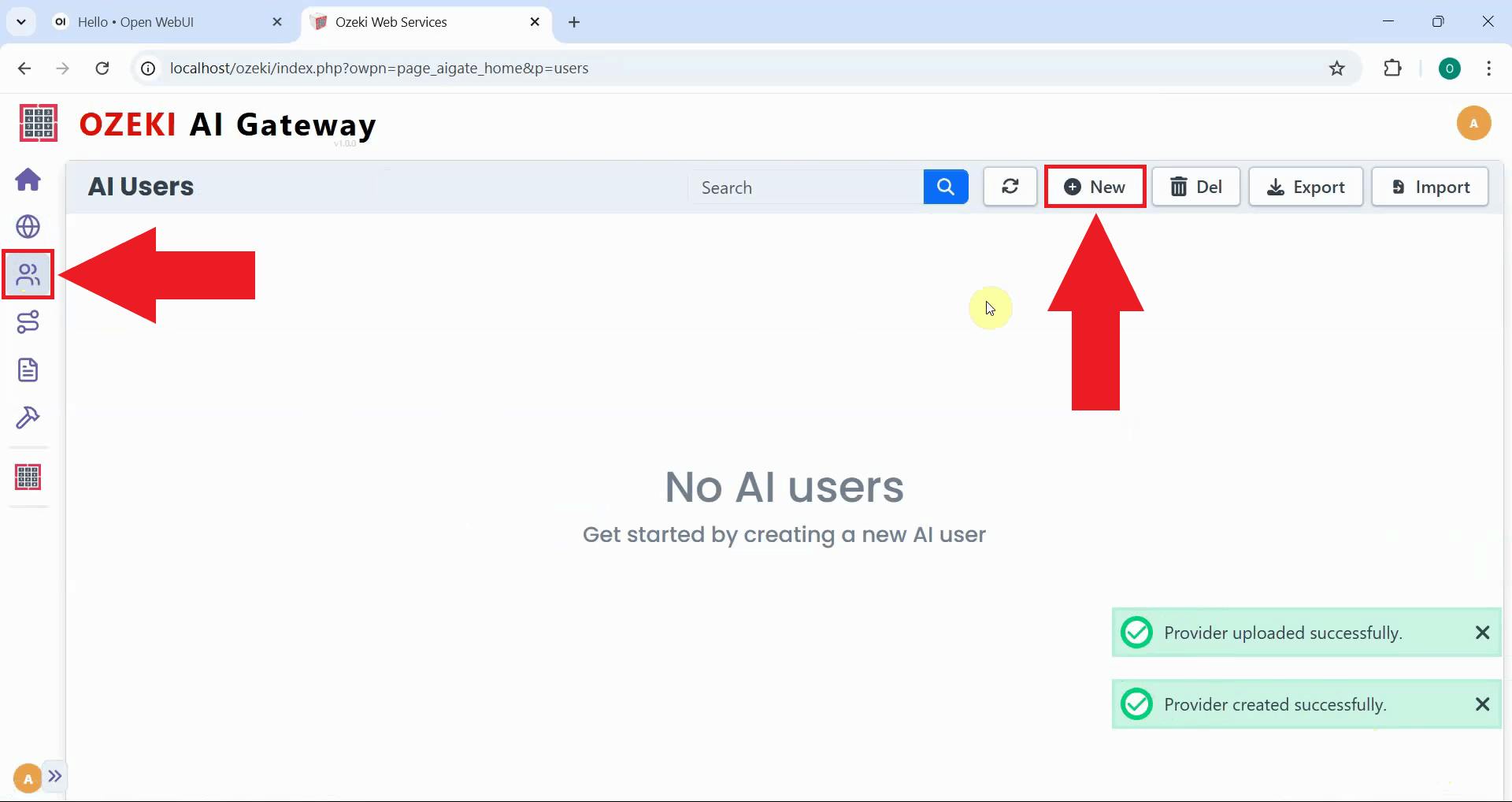
Step 2 - Create new user on AI Users page
Creating distinct user accounts allows you to control who can access your gateway. Click the "New" button to open the user creation form (Figure 5). Users represent the clients or applications that will authenticate with your gateway to send AI requests.
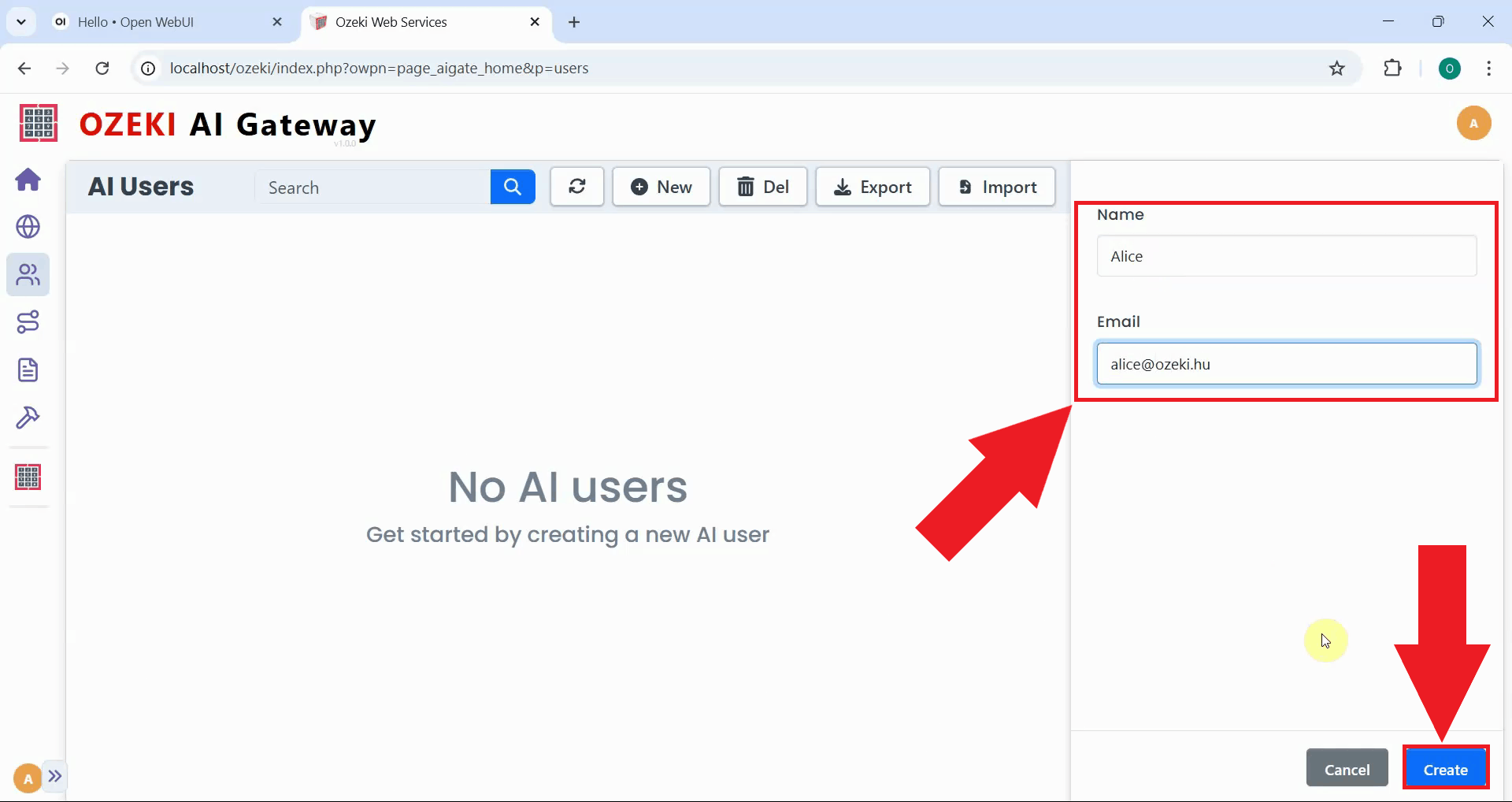
Fill in the user creation form with a username and email address. Click "Create" to save the user account and proceed to generate API credentials (Figure 6).
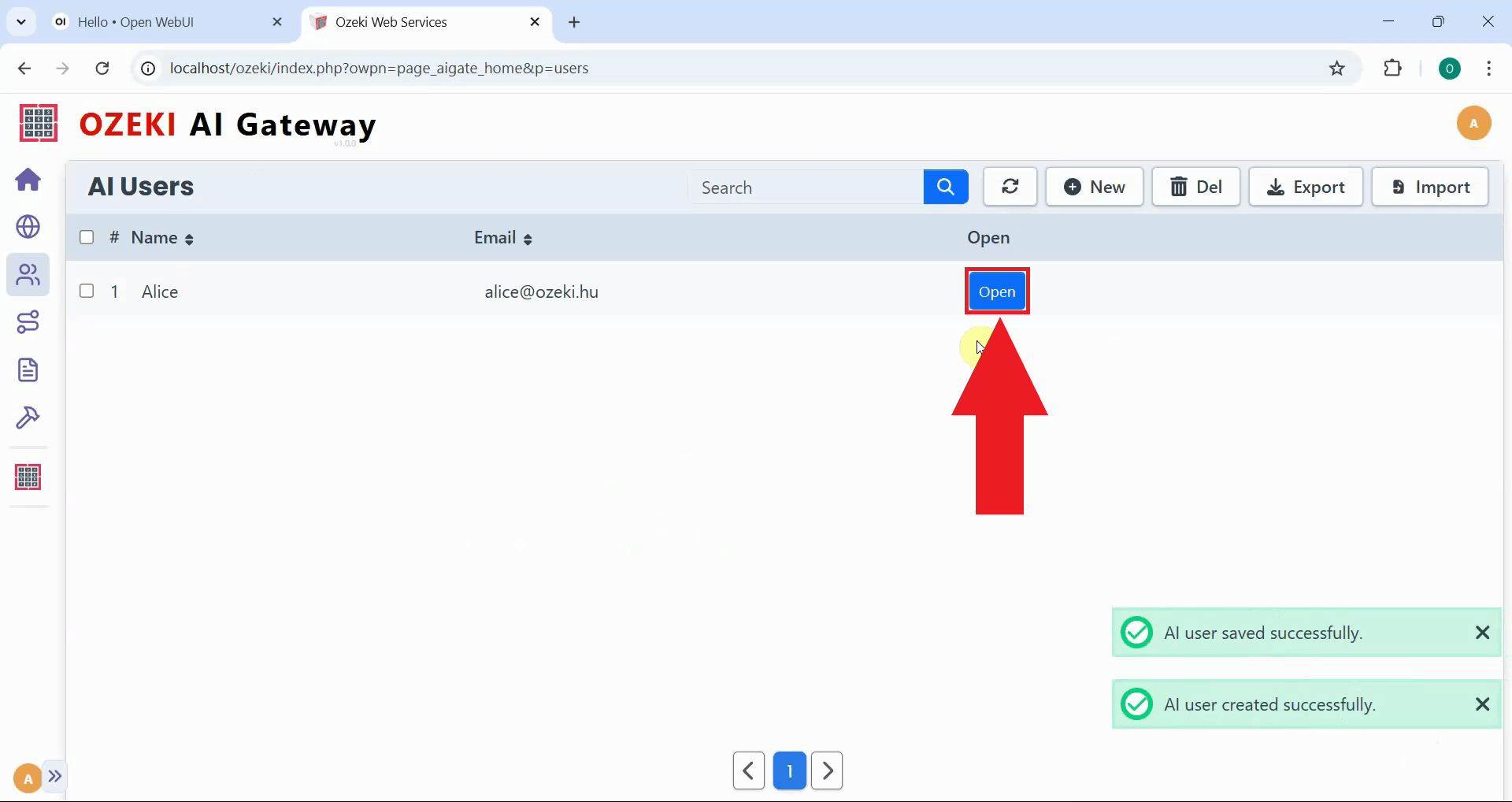
Step 3 - Create user API key
After creating the user, click the "Open" button to access their credential management page. The API keys page displays existing keys for the user and allows you to generate new ones. These keys authenticate requests from client applications to the gateway (Figure 7).
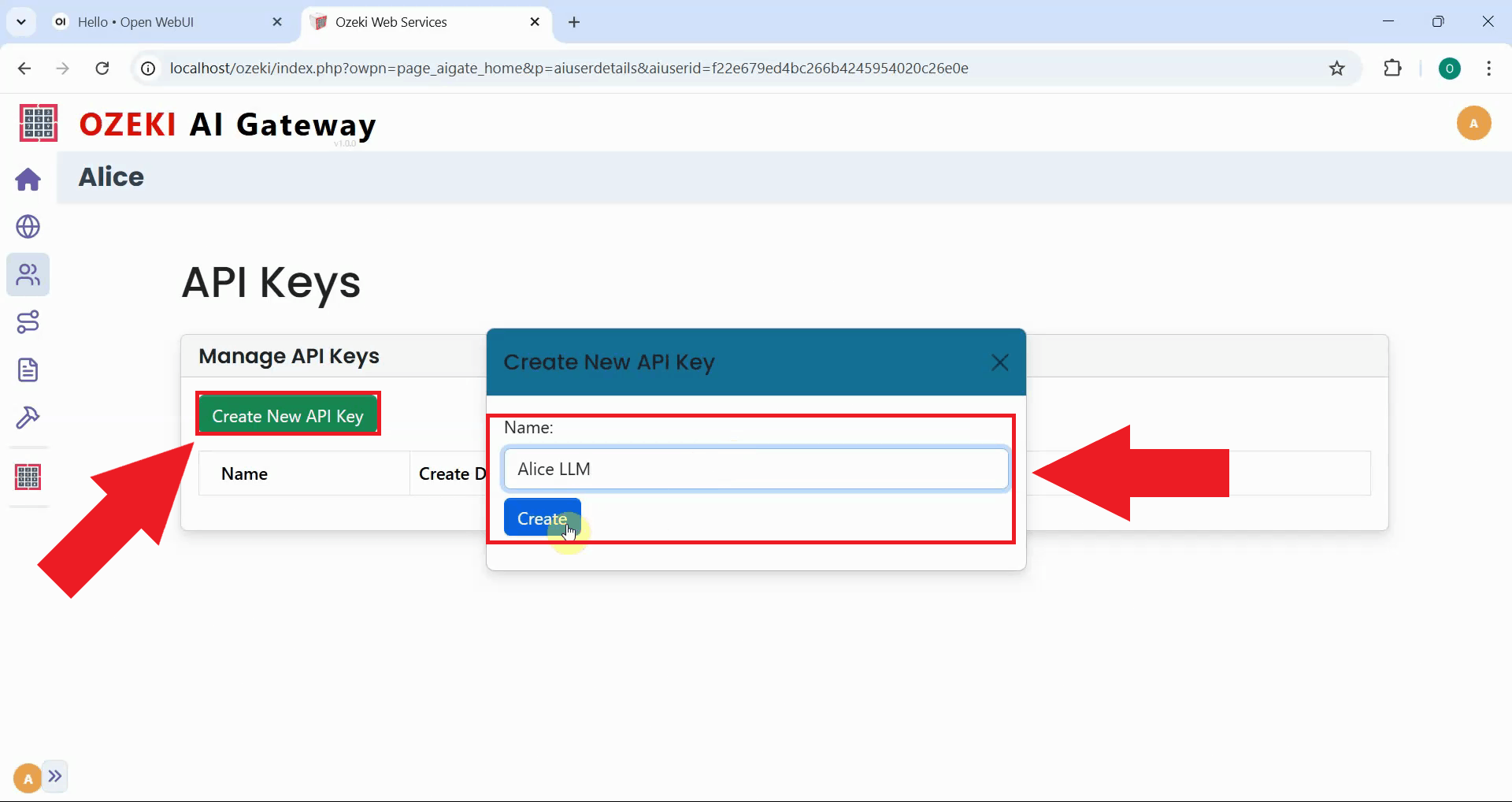
Click the "Create New API Key" button to create an API key for the user. Each user requires at least one API key to authenticate with the gateway when making API requests (Figure 8).
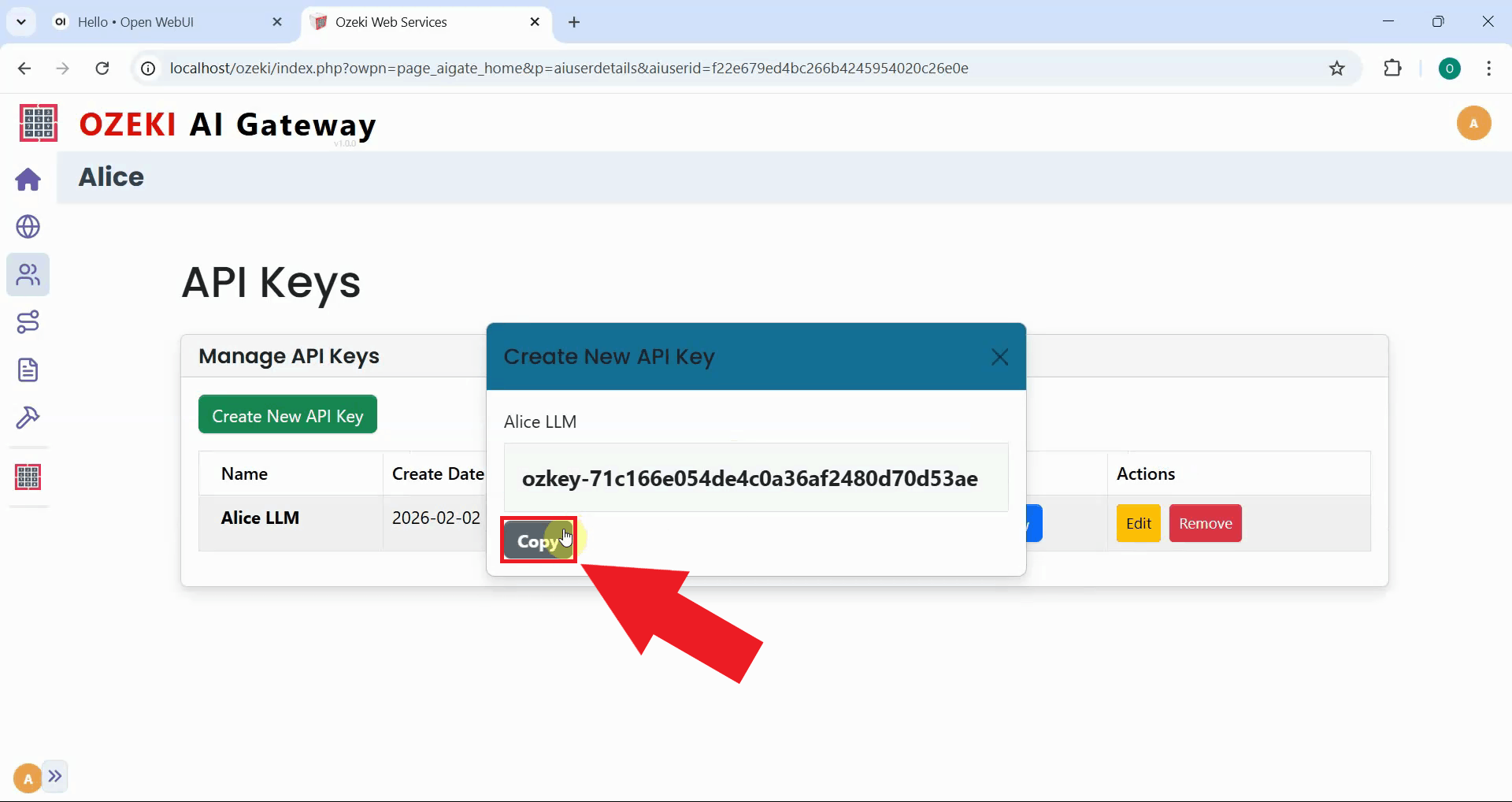
After the key is generated, click the copy button to save it to your clipboard. Store this key securely as you'll need it to configure a connection to the gateway (Figure 9).
Step 4 - Create a new route
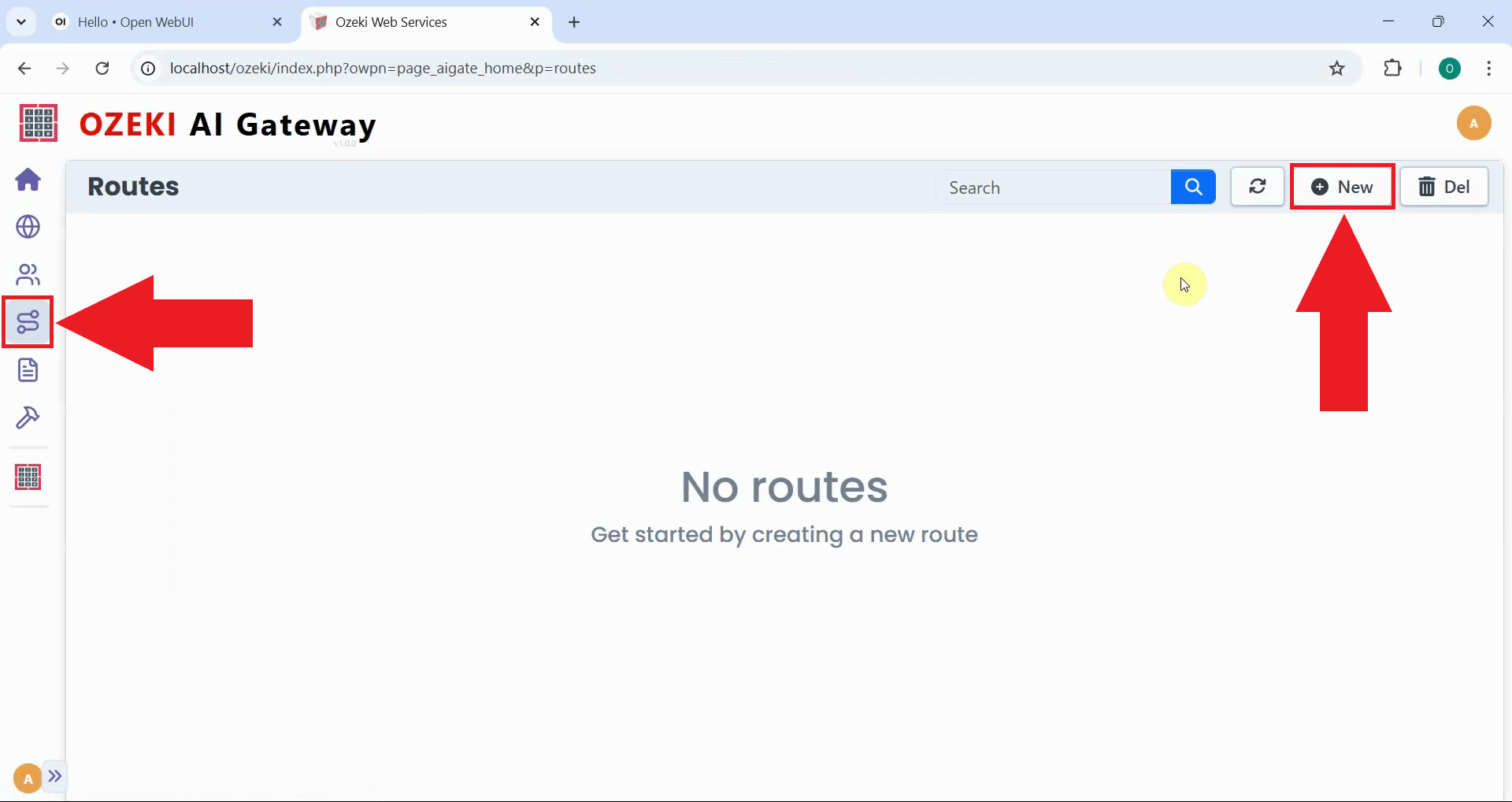
Navigate to the Routes page to create routing rules. Routes define the mapping between users, providers, and API models, determining which users can access which AI models through which providers. Click the "New" button to open the route creation form (Figure 10).
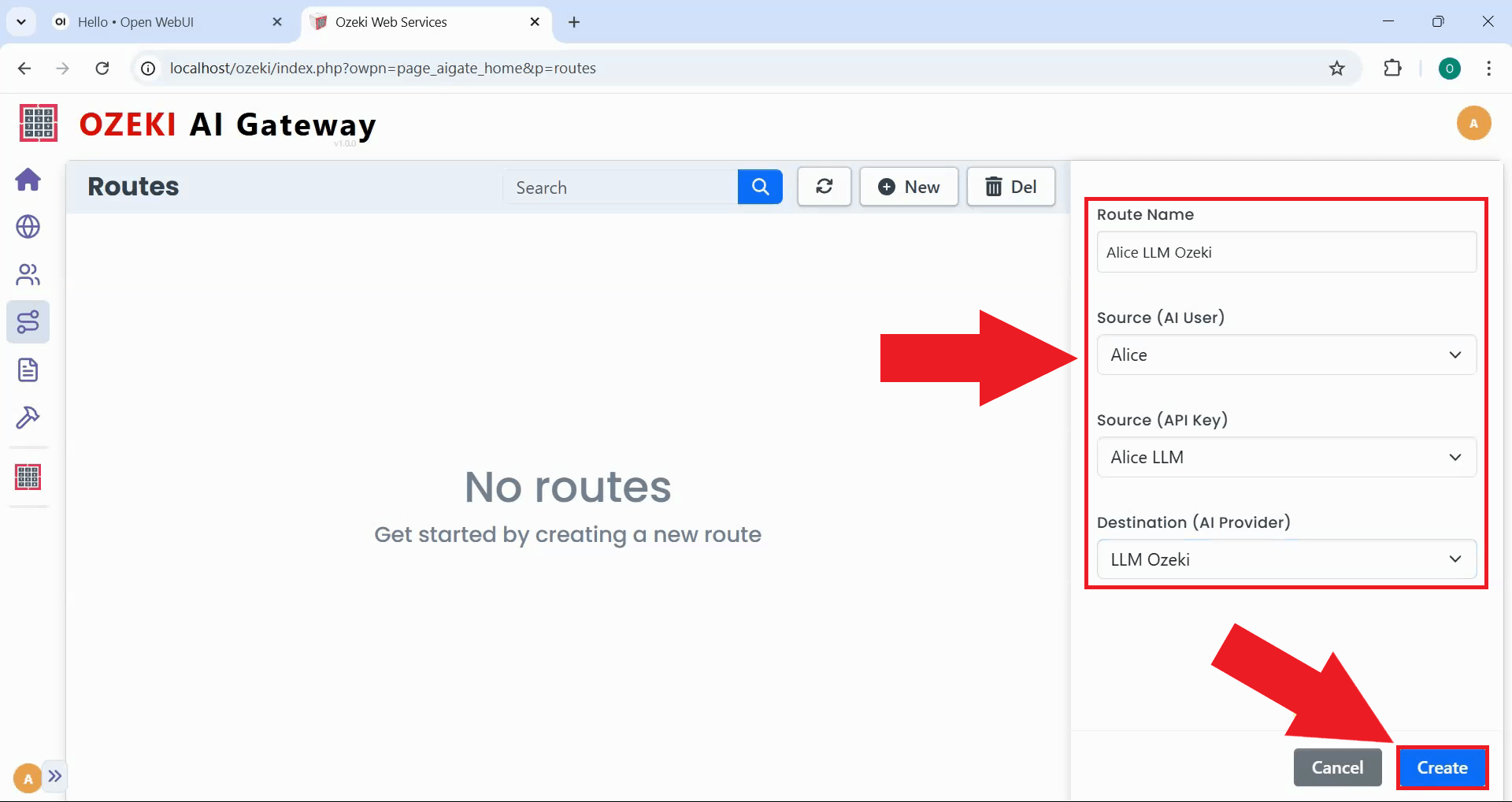
Specify the route configuration by selecting the user, provider, and model information from dropdown menus. The route includes the user account, the AI provider through which requests will be routed, and the specific models that this user can access. Click "Create" to register this access path in the gateway's routing table (Figure 11).
Step 5 - Add new connection in Open WebUI
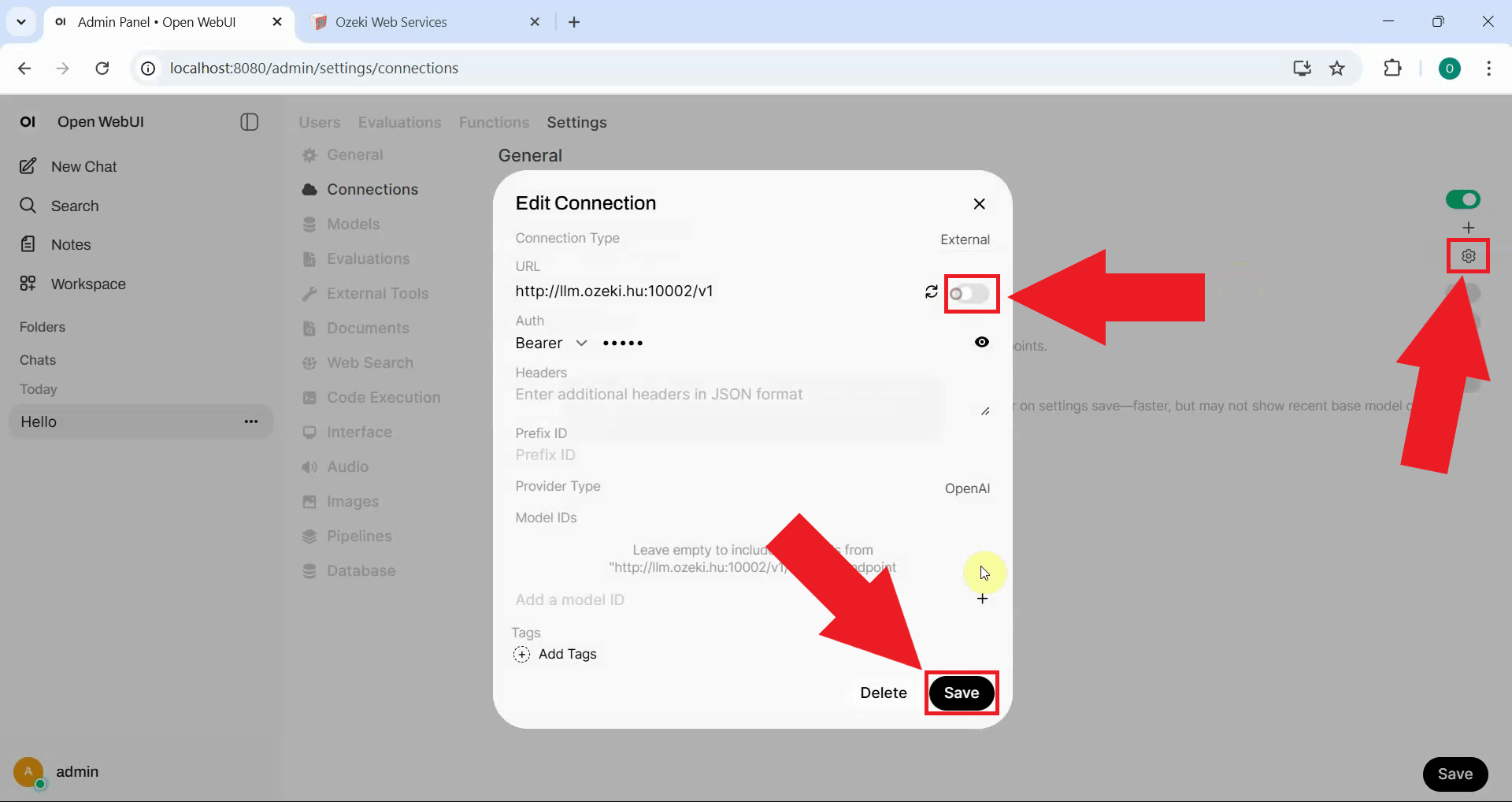
Return to Open WebUI and navigate to the Connections page in the admin panel. Locate the direct Kimi K2.5 connection you created previously and disable or delete it (Figure 12).
Click "Add Connection" in Open WebUI to create a new connection that points to Ozeki AI Gateway. This connection will route all model requests through the gateway instead of directly to Kimi K2.5 (Figure 13).
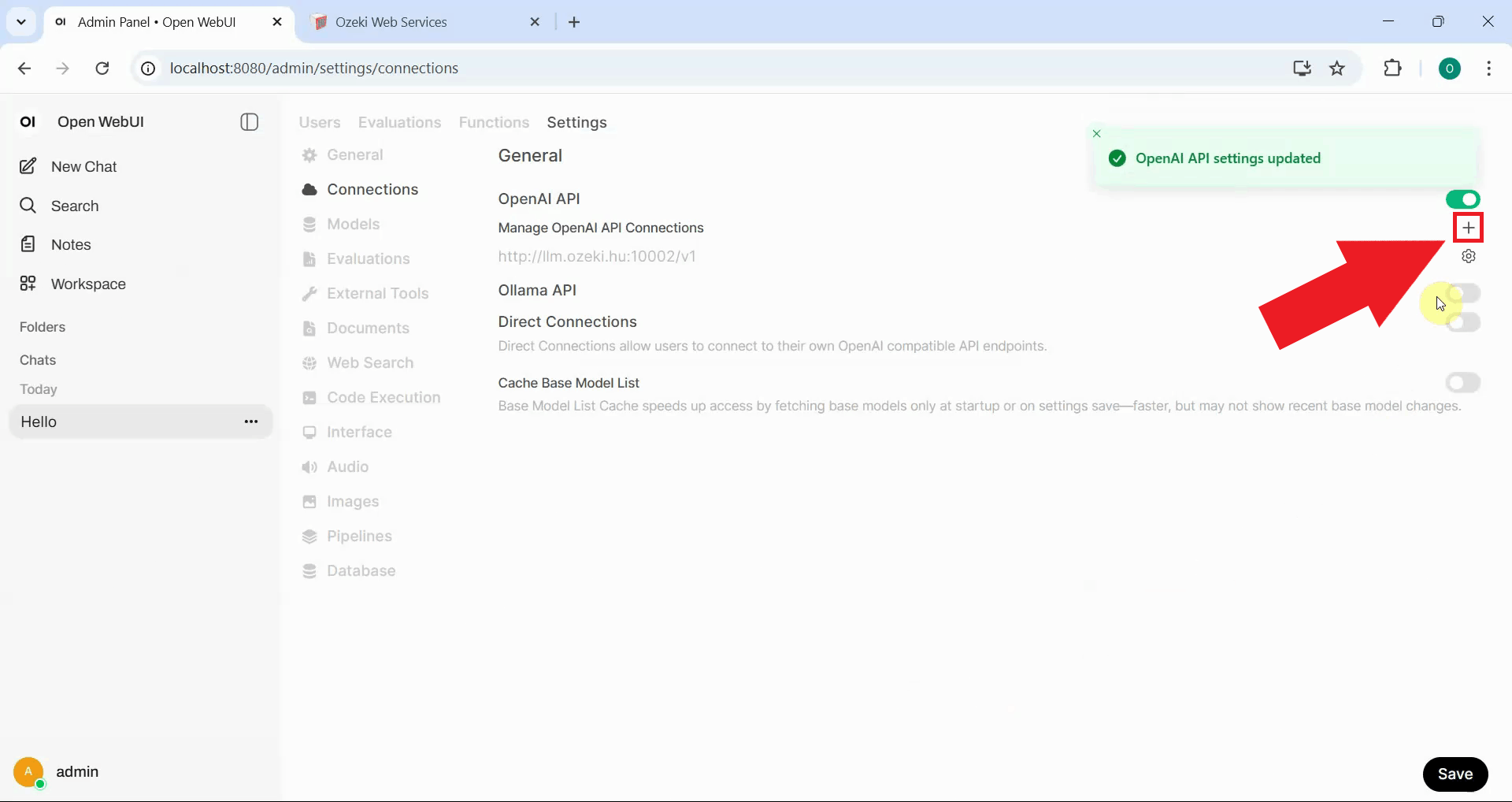
Fill in the connection form with Ozeki AI Gateway's URL, paste the API key you copied earlier and save the configuration. Open WebUI will now route your requests through the gateway which will forward them to Kimi K2.5 (Figure 14).
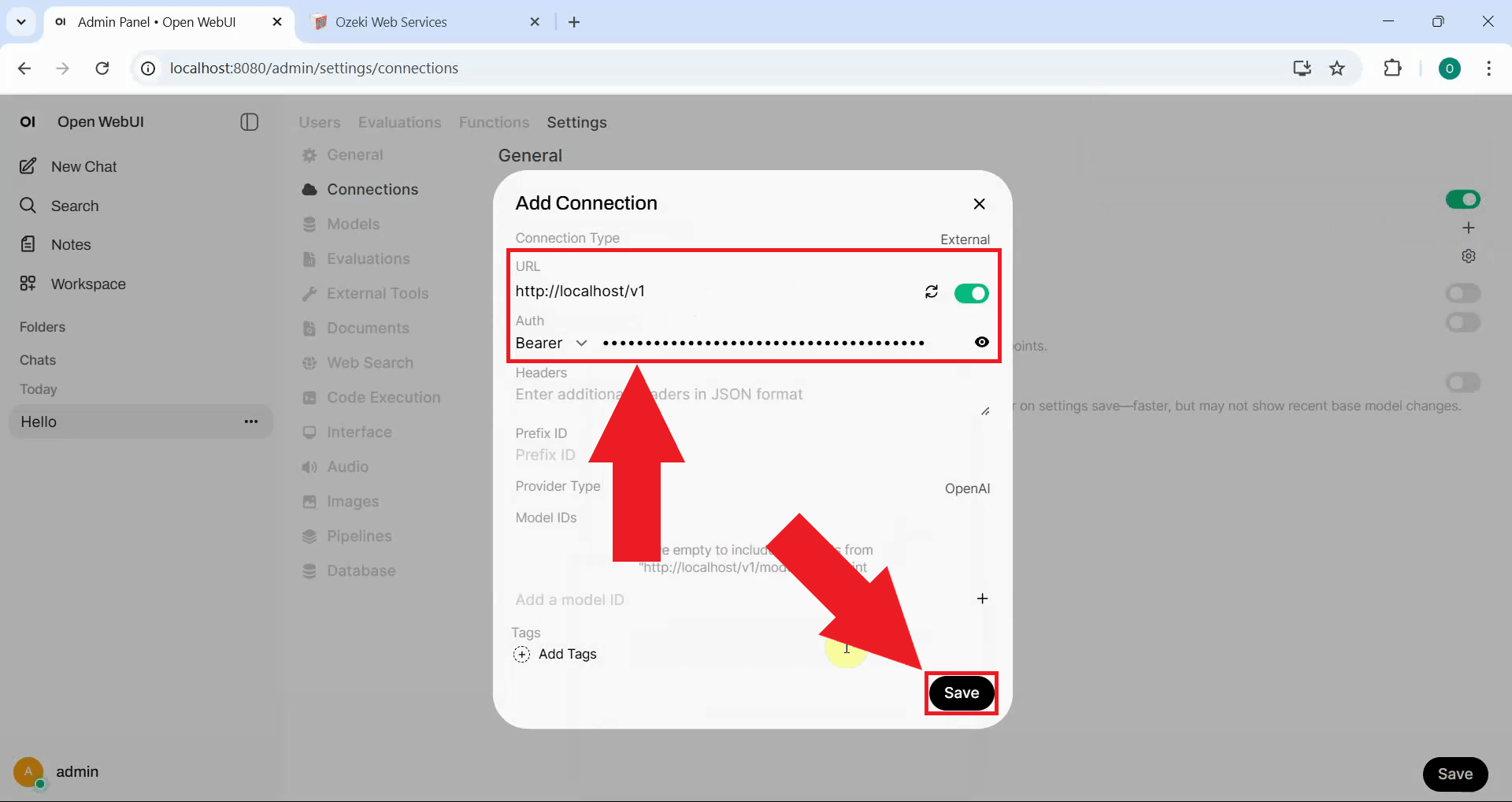
Step 6 - Send test prompt to Kimi model
Return to the Open WebUI chat interface and send a test prompt to the AI model. The response will still contain the missing think tag issue since the route has no modifications configured (Figure 15).
Step 7 - Check logs in Ozeki AI Gateway
In your Ozeki AI Gateway web interface, navigate to the Logs page. This page displays user logs, system logs, and reports where all transaction data is stored and organized by date. Navigate to the folder that corresponds to when you sent your test prompt (Figure 16).
Click on the transaction entry to open the detailed log view. The log file contains the complete request sent from Open WebUI and the response received from Kimi K2.5 (Figure 17).
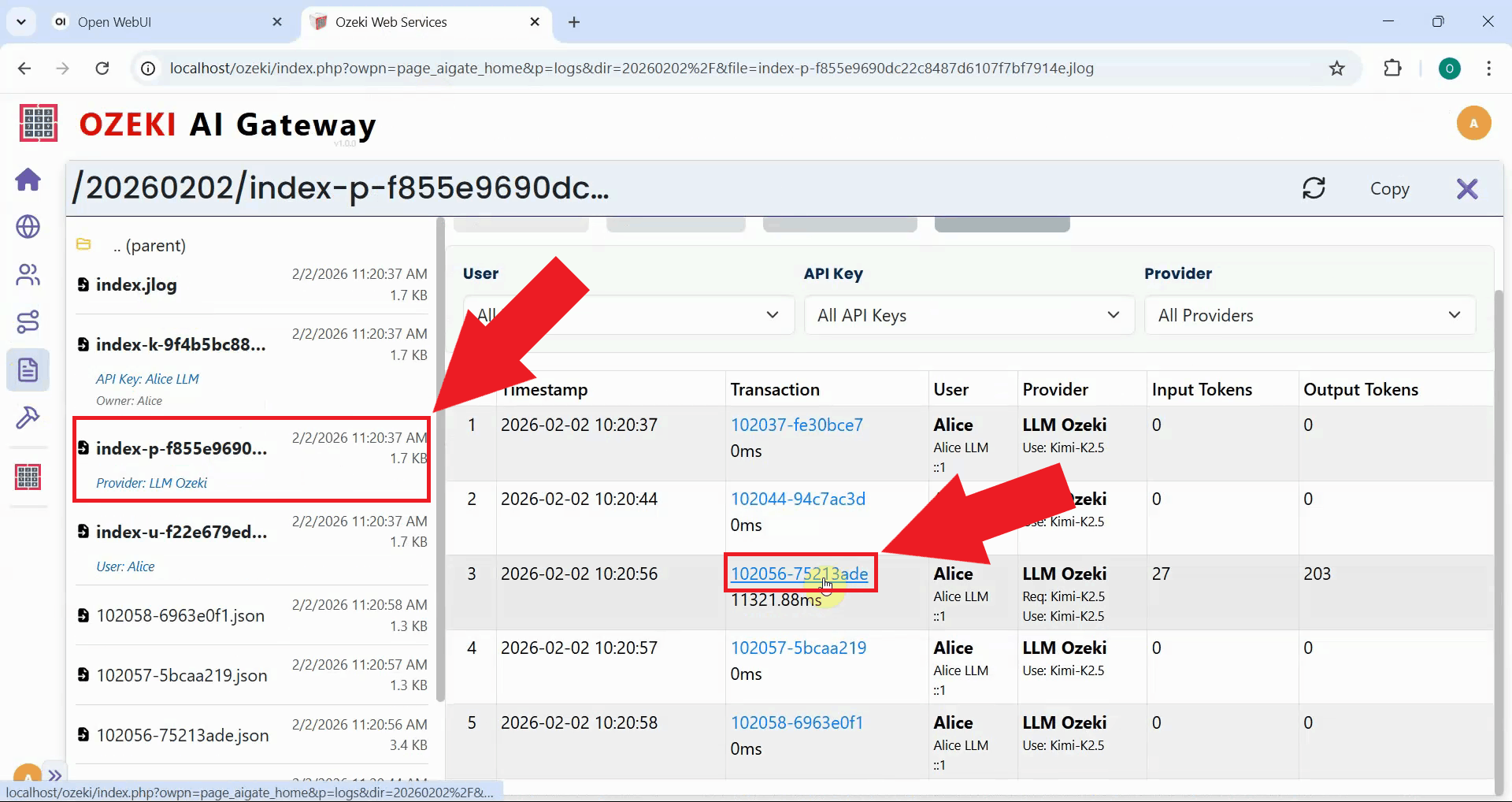
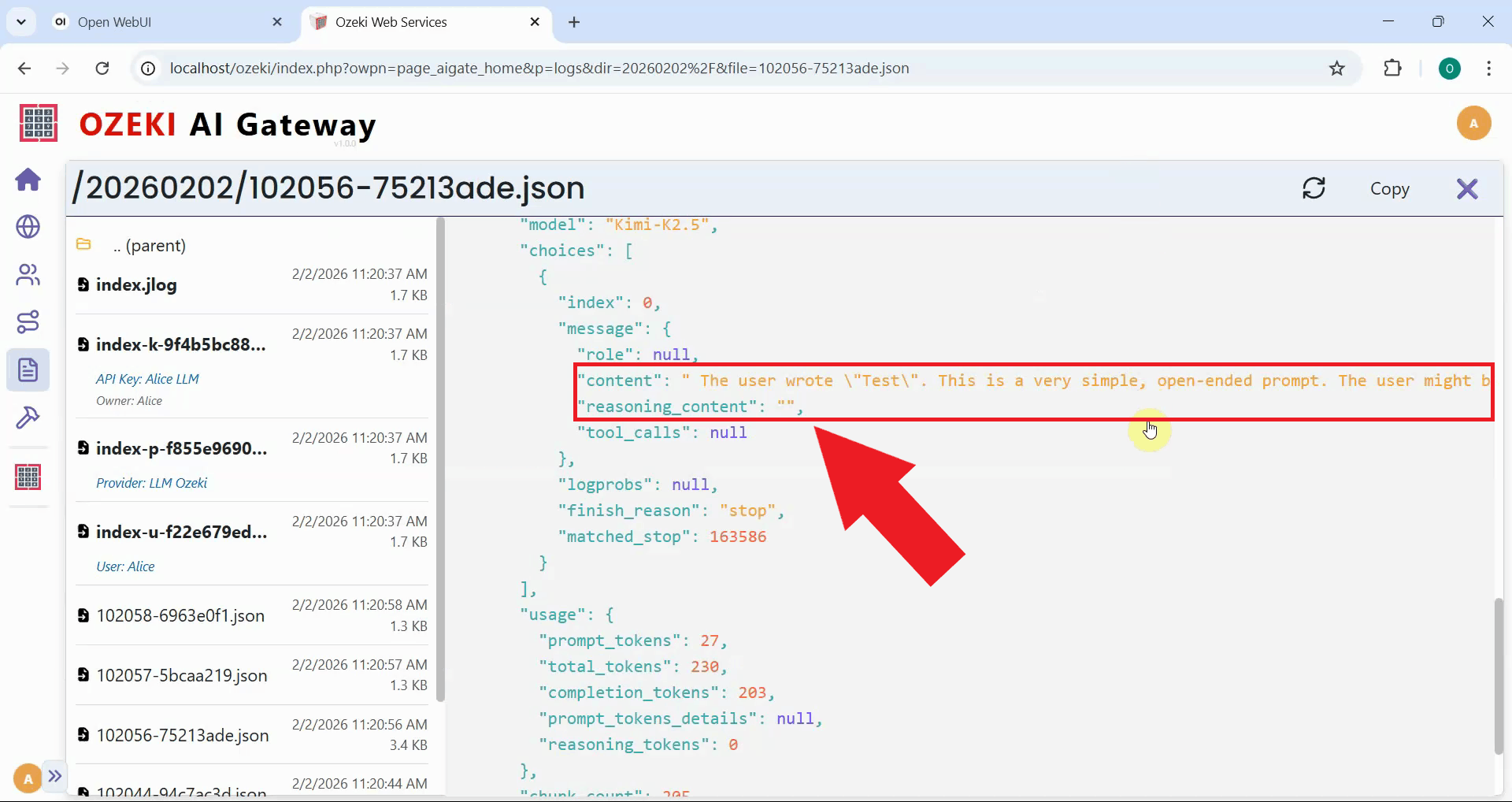
Examine the response section of the log file and locate the "reasoning_content" field. You'll notice it's empty even though the model generated reasoning text (Figure 18). The next step is to add request modifiers to the route.
Fix missing think tag using request modifiers (Video tutorial)
In this video tutorial, you will learn how to fix the missing think tag issue by configuring a request modifier in Ozeki AI Gateway. The video demonstrates editing the route to add a custom property that injects the "thinking: true" parameter into requests, enabling proper parsing of reasoning content.
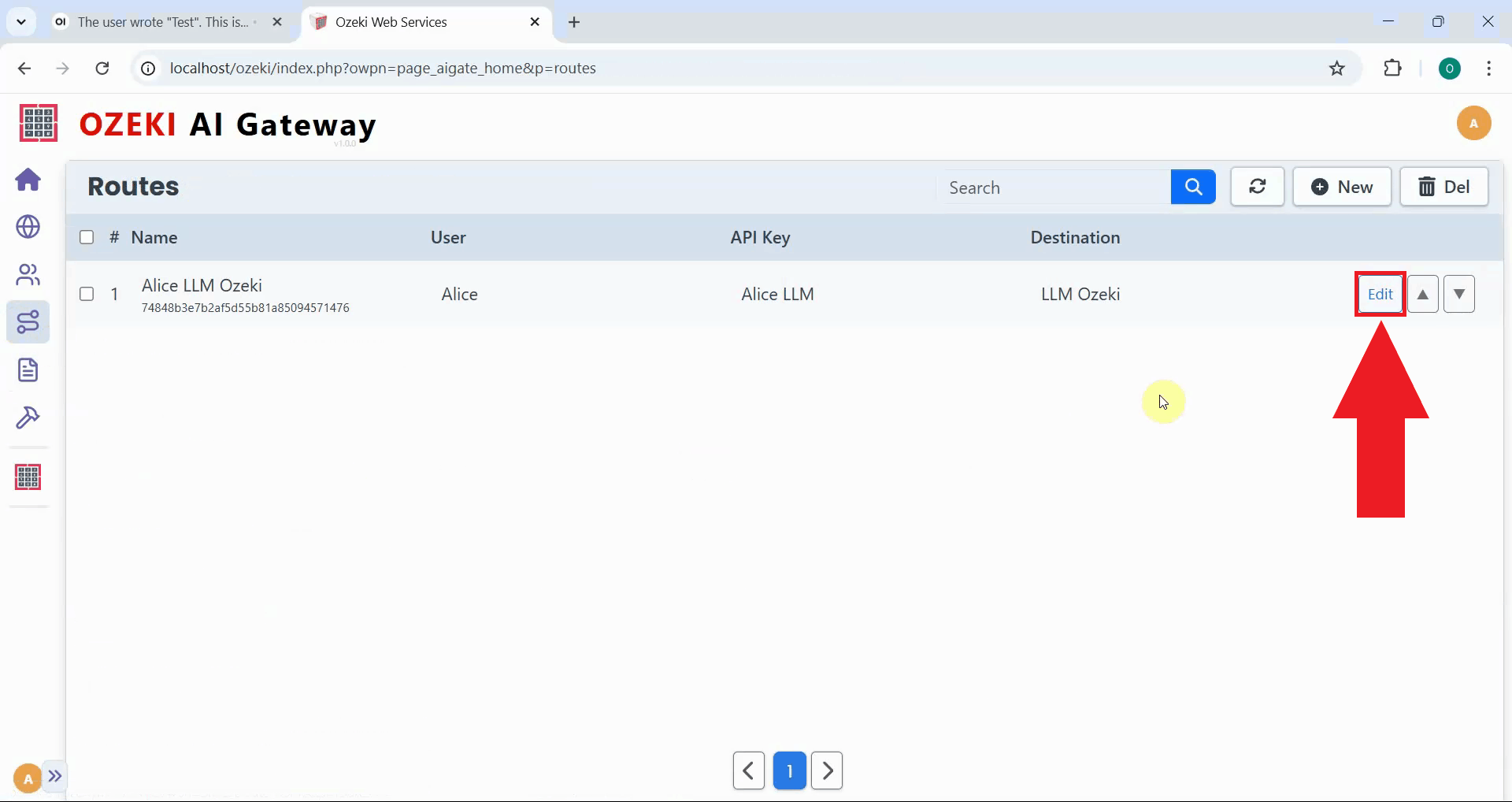
Step 8 - Add route request modifier
Navigate to the Routes page in Ozeki AI Gateway and locate the route you created earlier. Click the "Edit" button to open the configuration form where you can modify route settings and add request modifiers to resolve the missing think tag issue (Figure 19).
Switch to the Advanced tab in the route configuration form and locate the Request Modifiers section. Click "Add" to create a new request modification rule (Figure 20).
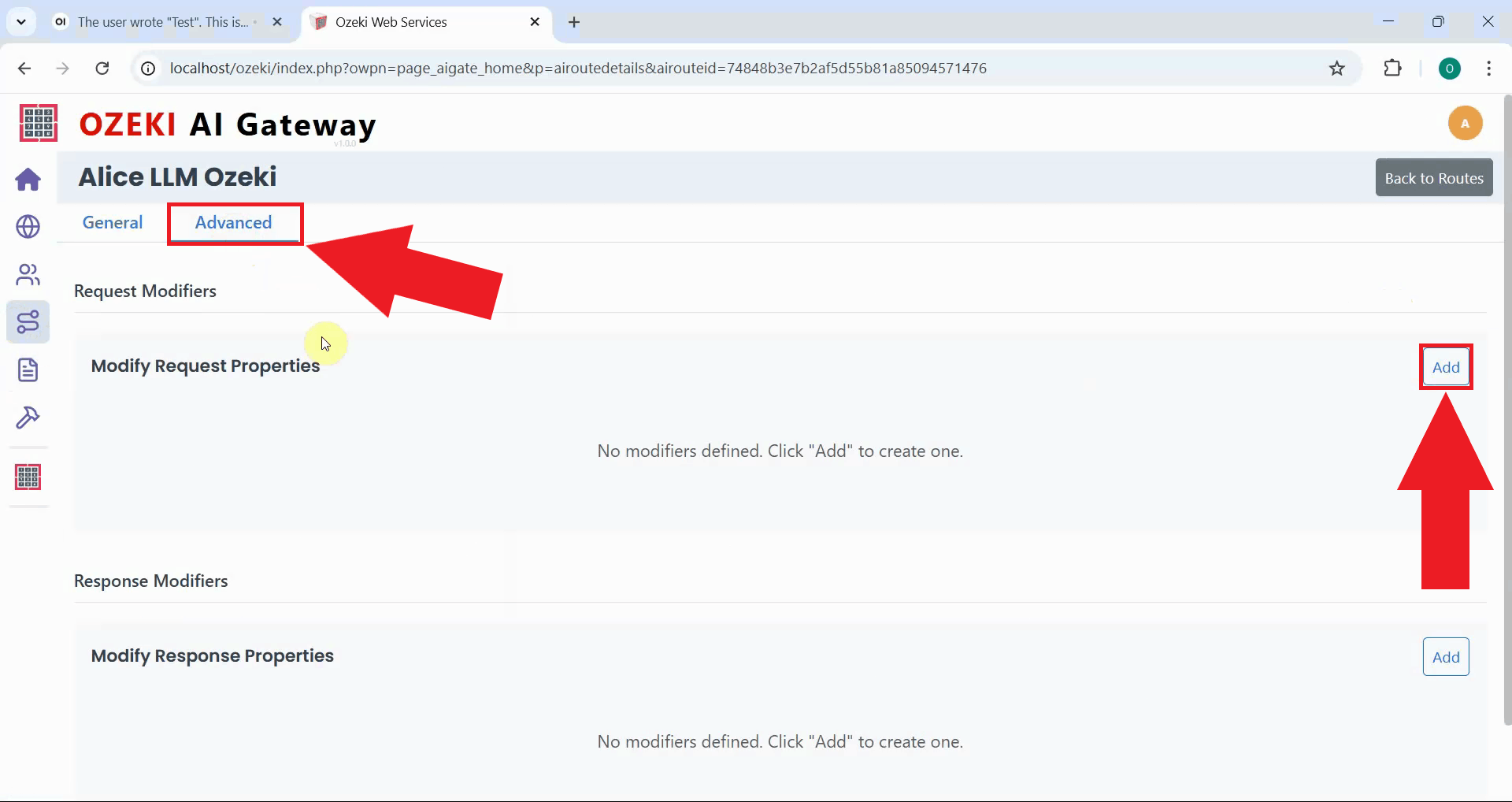
Step 9 - Create custom modifier
In the request modifier form, select "Custom" from the Property dropdown menu. Custom properties enable precise control over request parameters sent to the AI model (Figure 21).
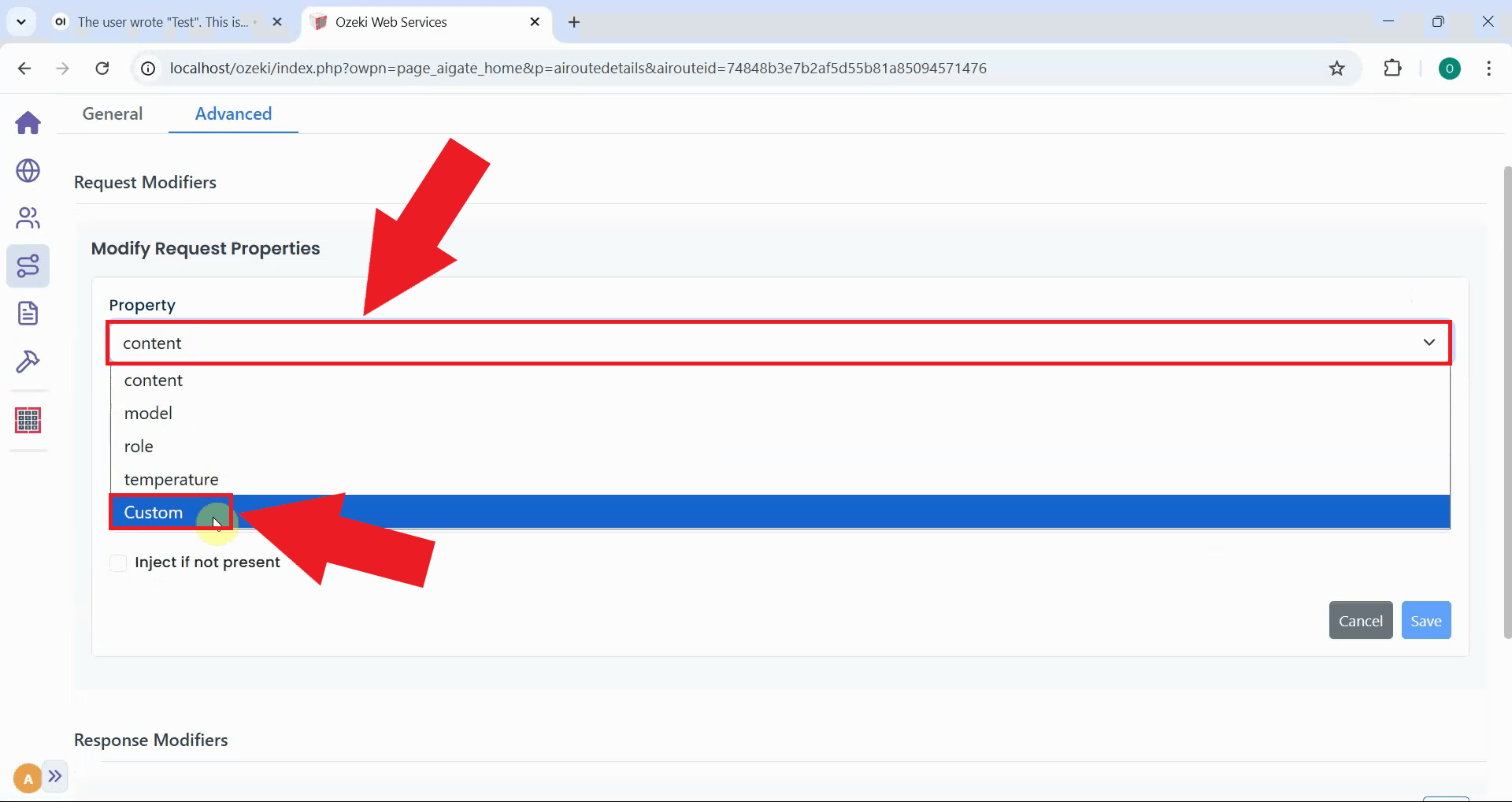
Fill in the custom property configuration fields with the following values:
- Custom Property Name:
chat_template_kwargs - Match (Regex):
/^.*/ - Replace:
{"thinking": true}
This configuration injects the "thinking" parameter that tells Kimi K2.5 to format its reasoning output with proper opening and closing tags (Figure 22).
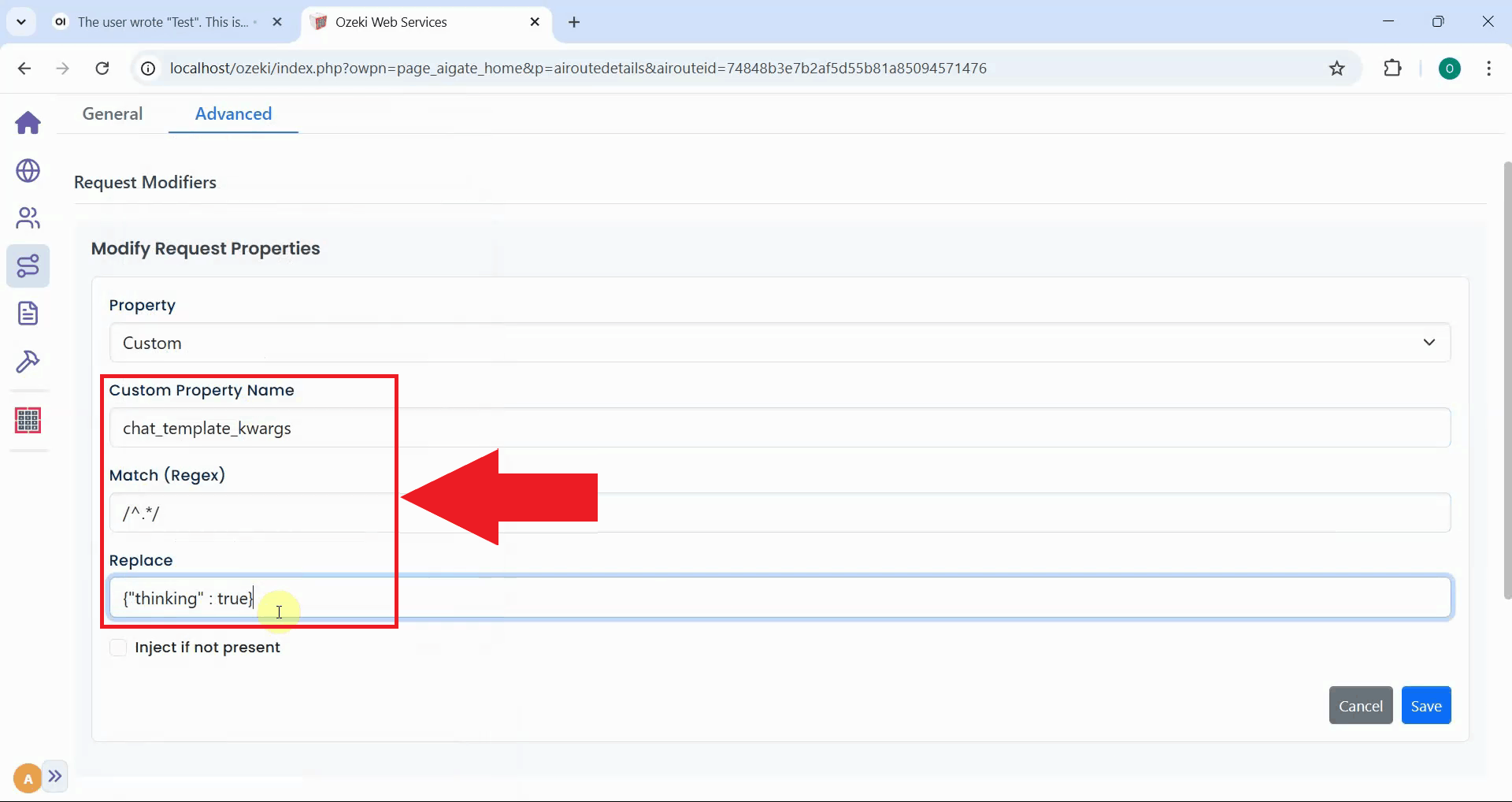
Check the "Inject if not present" checkbox to ensure the property is added even if it doesn't exist in the original request. Click "Save" to apply the modifier and close the configuration dialog (Figure 23).
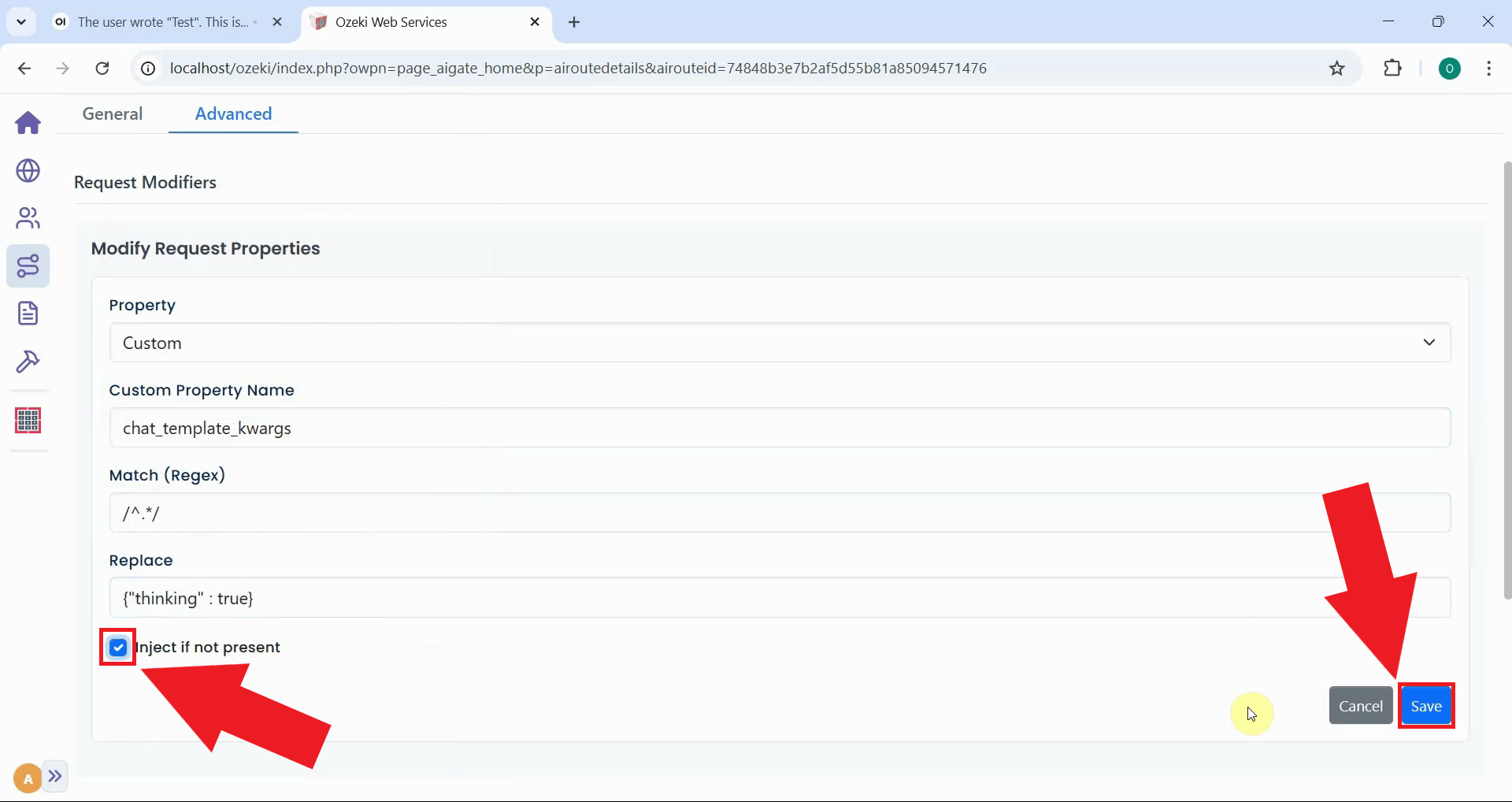
Step 10 - Send test prompt and verify response
Return to Open WebUI and send a test prompt for the AI model. The request now includes the thinking parameter injected by the gateway's request modifier. This should trigger Kimi K2.5 to format its reasoning output correctly with both opening and closing think tags (Figure 24).
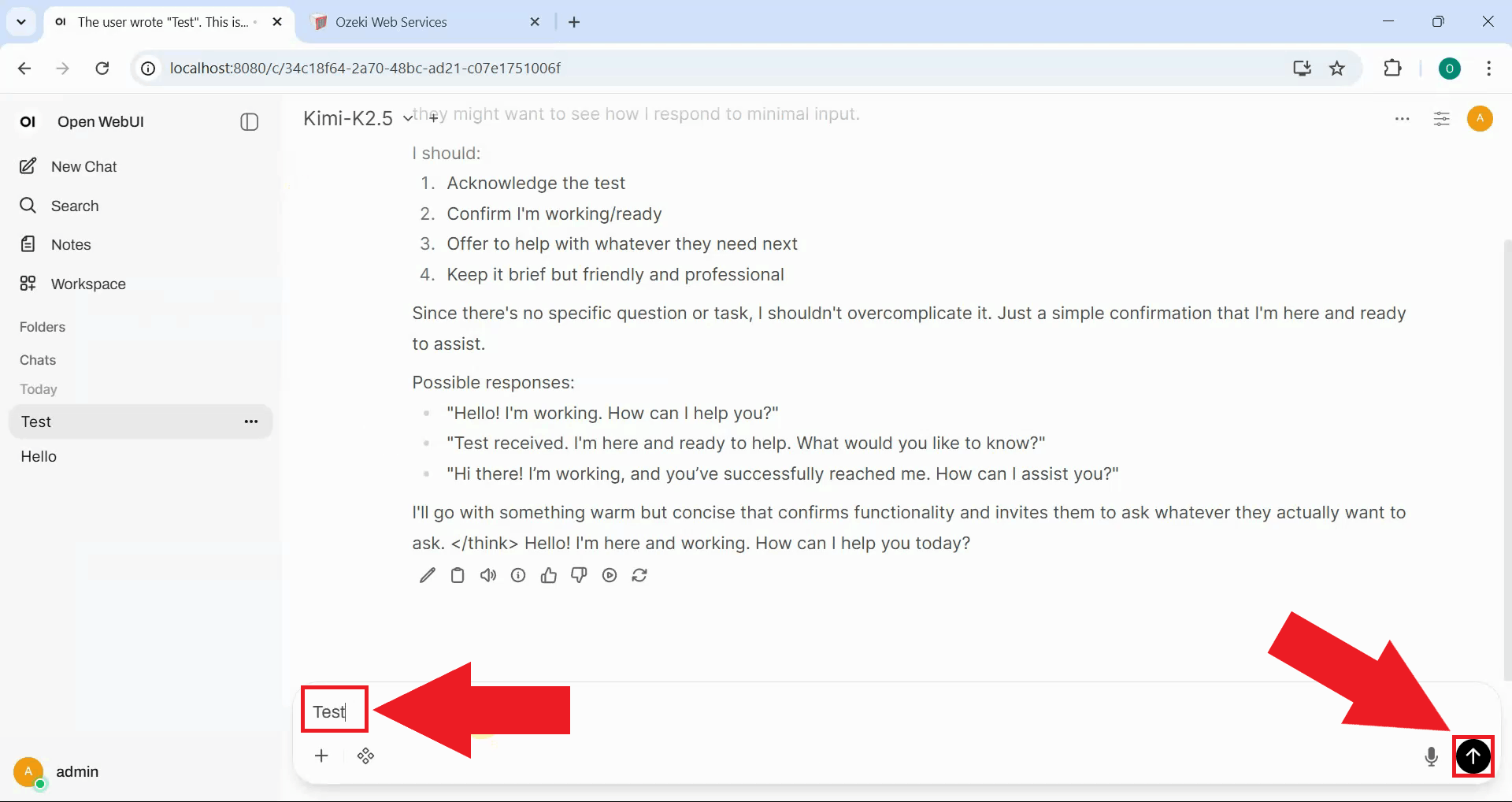
Examine the response in Open WebUI and notice that the reasoning content now appears properly formatted. The thinking process is separated into a collapsible section that can be expanded or collapsed (Figure 25).
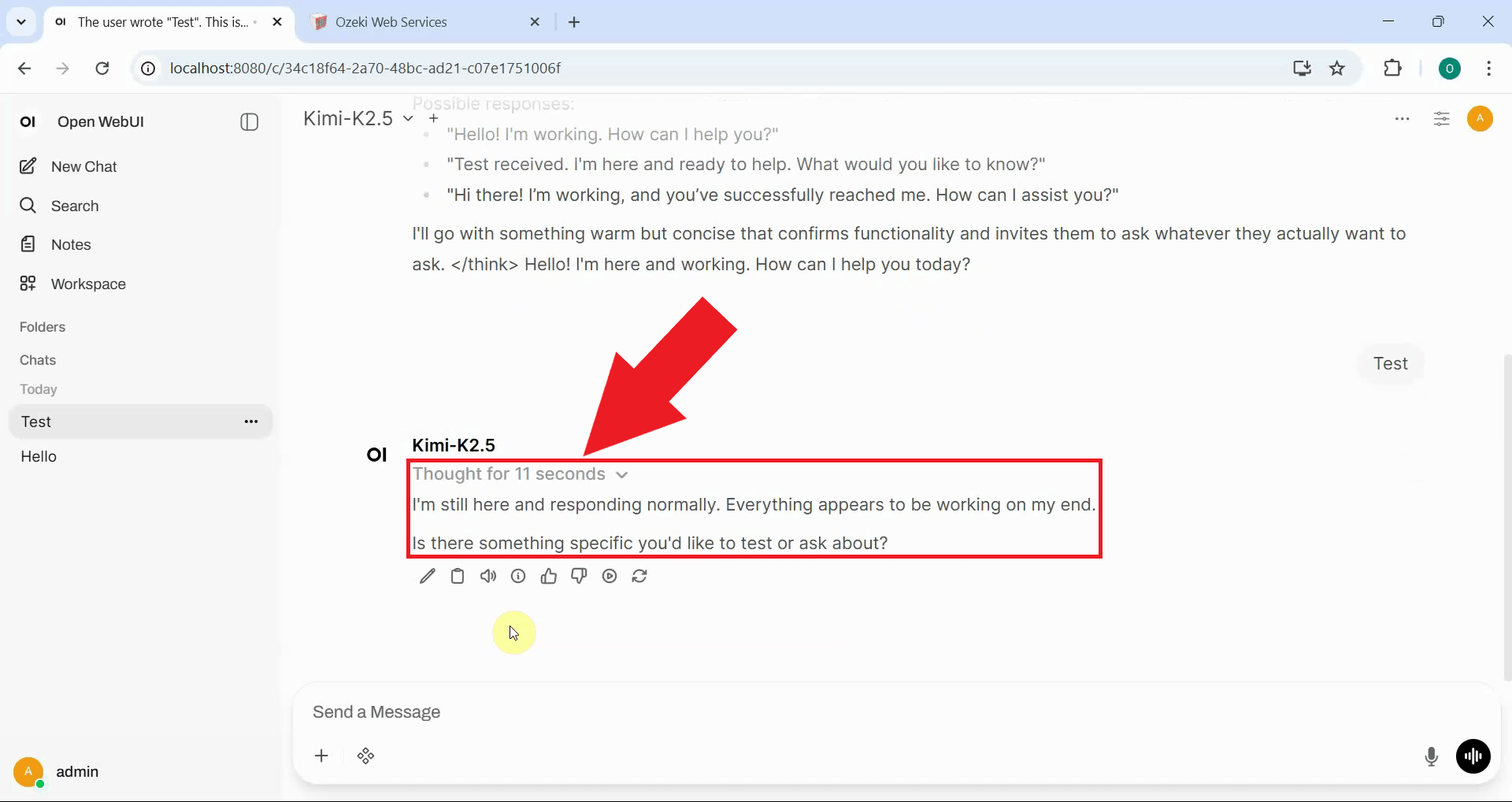
Step 11 - Check logs in Ozeki AI Gateway
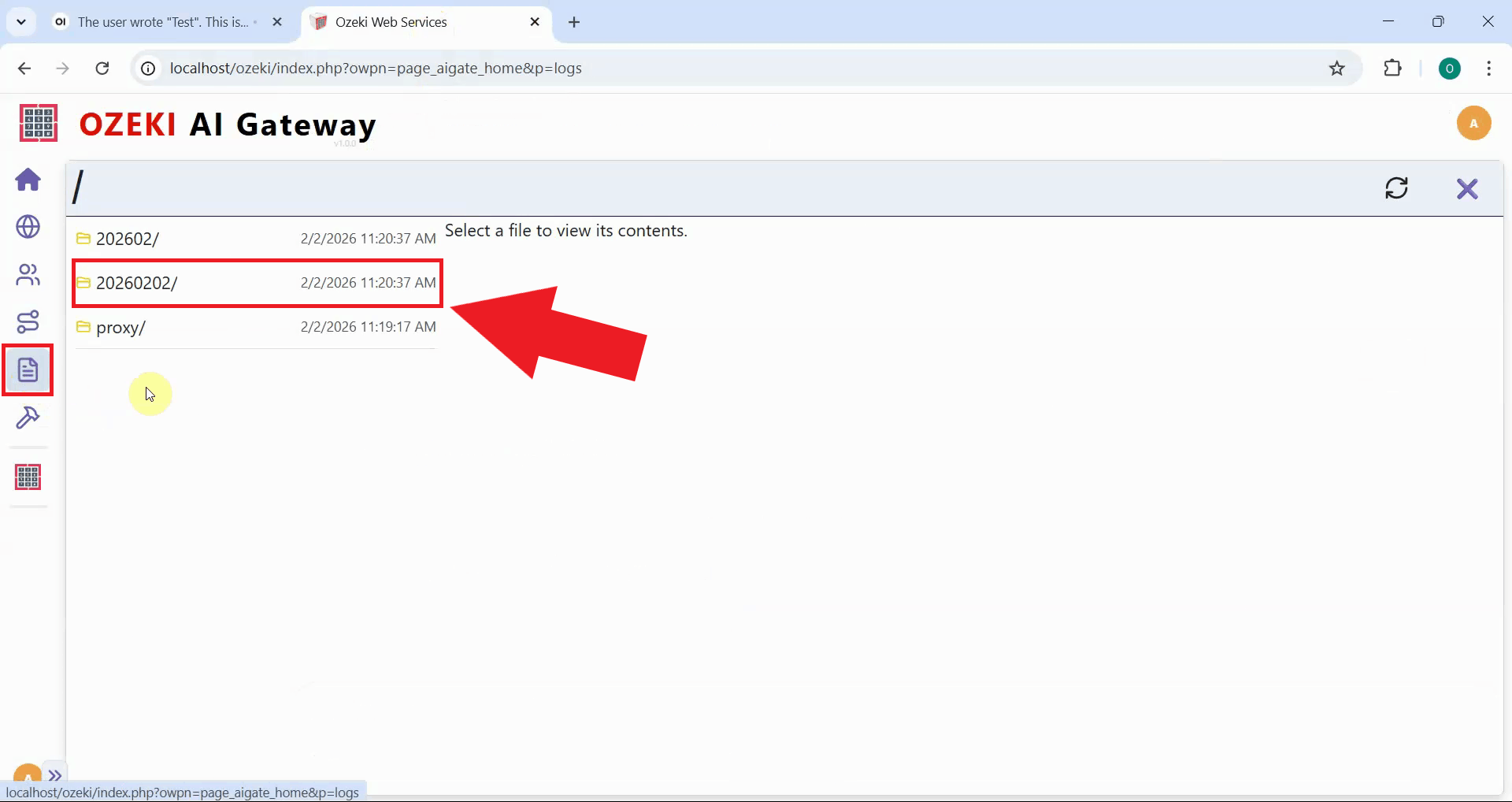
In your Ozeki AI Gateway web interface, navigate to the Logs page. This page displays user logs, system logs, and reports where all transaction data is stored and organized by date. Navigate to the folder that corresponds to when you sent your test prompt (Figure 26).
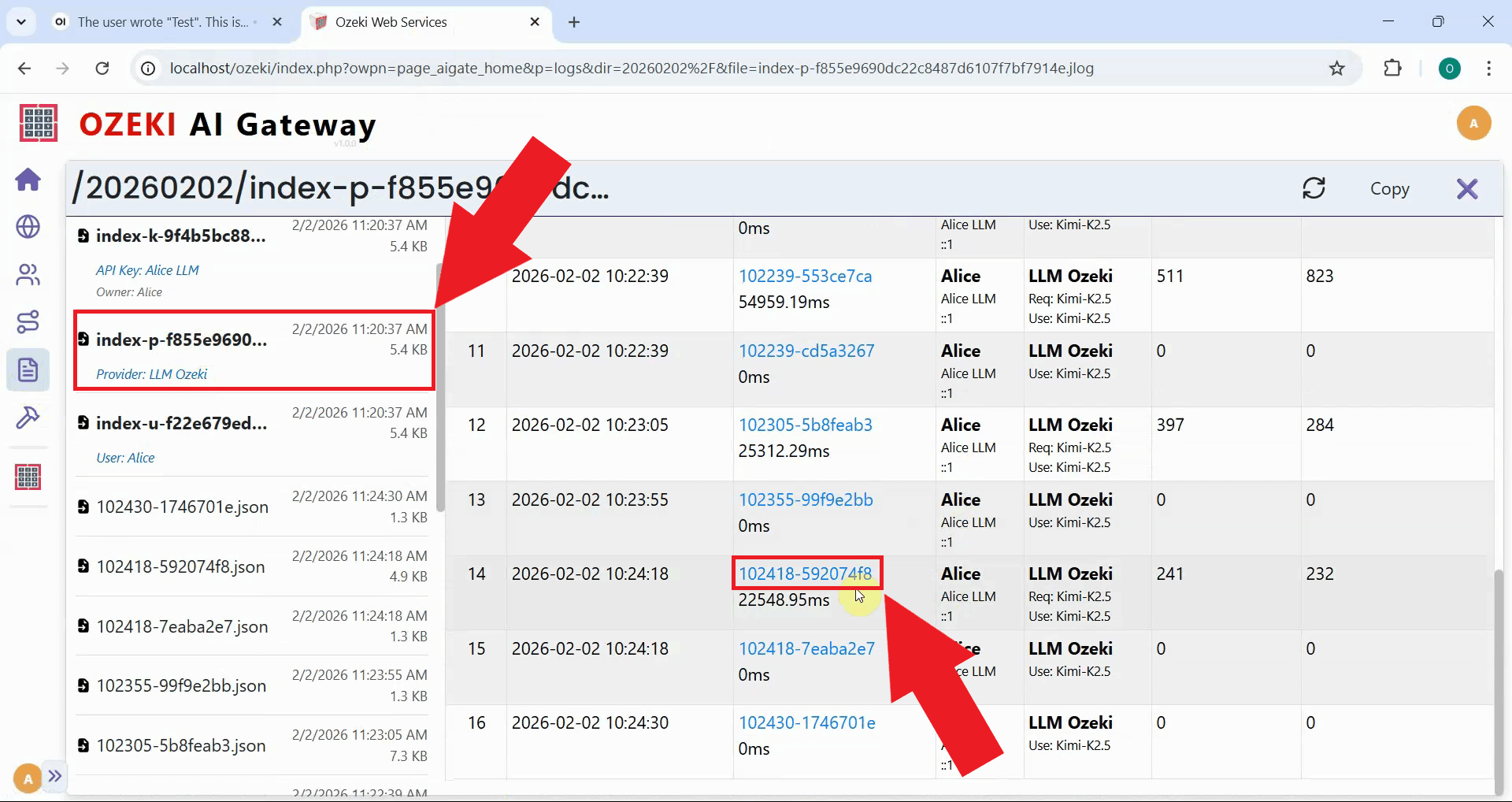
Click on the transaction entry to view the complete request and response data. You can verify that the chat_template_kwargs property was successfully injected with the thinking parameter (Figure 27).
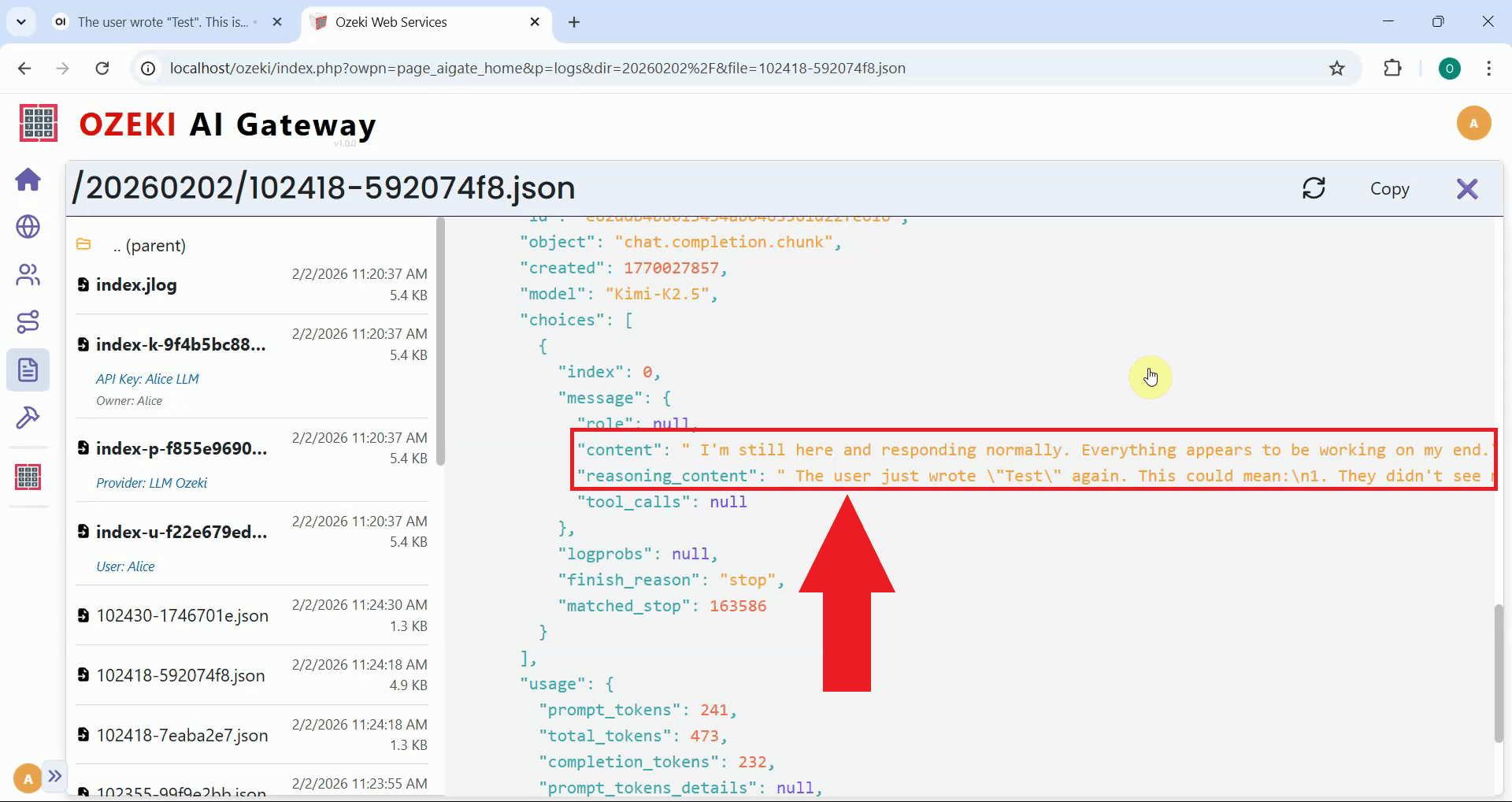
In the transaction file, locate the "reasoning_content" field. Unlike before, this field now contains the reasoning text properly extracted from the response. This confirms that the request modifier successfully fixed the missing think tag issue, allowing proper parsing of the model's reasoning process (Figure 28).
To sum it up
You have successfully resolved the missing think tag issue for Kimi K2.5 by configuring Ozeki AI Gateway
with a request modifier. The gateway now automatically injects the {"thinking": true} parameter
into requests, enabling Kimi K2.5 to properly format its reasoning output with both opening and closing think
tags. This solution works seamlessly with Open WebUI and other clients that require properly formatted
reasoning blocks, eliminating the need to modify the model or client applications directly.
This solution is particularly valuable for users who cannot modify their Kimi K2.5 server configuration or for those who need a centralized fix that works across multiple client applications.
