Android softphone: Make and accept calls
In the following example project you will see how to create a new Xamarin Android application in Visual Studio which is able to make and receive calls. For the example project you will need the Ozeki Android SDK, and Visual Studio Community installed. Let's create our first android softphone application.
Related: VoIP SIP make phone calls. If also you wish to build VoIP softphone on Windows, you might also be interested in a similar document, the VoIP SIP Making and Acceptcing calls in Ozeki VoIP SDK for Windows
What is a softphone?
Basically, a softphone is a type of software-based phone. It allows you to make phone calls over an internet connection without needing designated physical hardware, and it can be installed on desktops and mobile devices. In short, softphones help you make telephone calls without an actual telephone.
What is Xamarin?
Xamarin is an open-source platform for building modern and performant applications for iOS, Android, and Windows with .NET. Xamarin is an abstraction layer that manages communication of shared code with underlying platform code. Xamarin runs in a managed environment that provides conveniences such as memory allocation and garbage collection. Xamarin enables developers to share an average of 90% of their application across platforms. This pattern allows developers to write all of their business logic in a single language (or reuse existing application code) but achieve native performance, look, and feel on each platform.
What is Ozeki Phone System
Ozeki Phone System is software for Windows that transforms a computer into a communication server. Ozeki Phone System lets you build applications like PBX, VoIP gateway, IVR and ACD. It can be used for voice calls, video calls, SMS messaging and new-, revolutionary channels like real time communication through webbrowsers and mobile phones.
Quick steps
- Download and install the Ozeki Andorid SDK
- Create a new Xamarin Android application in Viusal Studio
- Add the OzekiSDK.dll as a reference to our project
- Create the layout of the application
- Create a Softphone class that implements the ISoftphone interface
- Create the MainActivity.cs activity which will ask for the login details
- Create the DialingActivity.cs activity which will be responsible for making and receiving calls
- Give microphone permission for your softphone application
- Debug your application (using a physical device or an emulator)
- Make your first call with the softphone based on the Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK
The 03_Call_Make_Accept.zip file
You can download the 03_Call_Make_Accept example application bellow,
and start to make and receive calls with it right now, or you can build
it yourself step by step to understand the base concept of the
Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK.
Download: 03_Call_Make_Accept.zip (2.16Mb)
Create a new Xamarin Android application in Visual Studio
To build our softphone application, we will create a new Xamarin Andorid project. In the following video I'll show you how to create a new Xamarin application in Visual Studio.
How to add the OzekiSDK.dll to our project as a reference
In order to use the contents of the Ozeki.VoIP and Ozeki.Media namespaces, we have to include the OzekiSDK.dll in our project. In the following video I'll show you how to add the OzekiSDK.dll reference to your project. You can find the OzekiSDK.dll file in the following place: C:\Program Files\Ozeki\Ozeki SDK for Android\SDK\MonoAndroid.
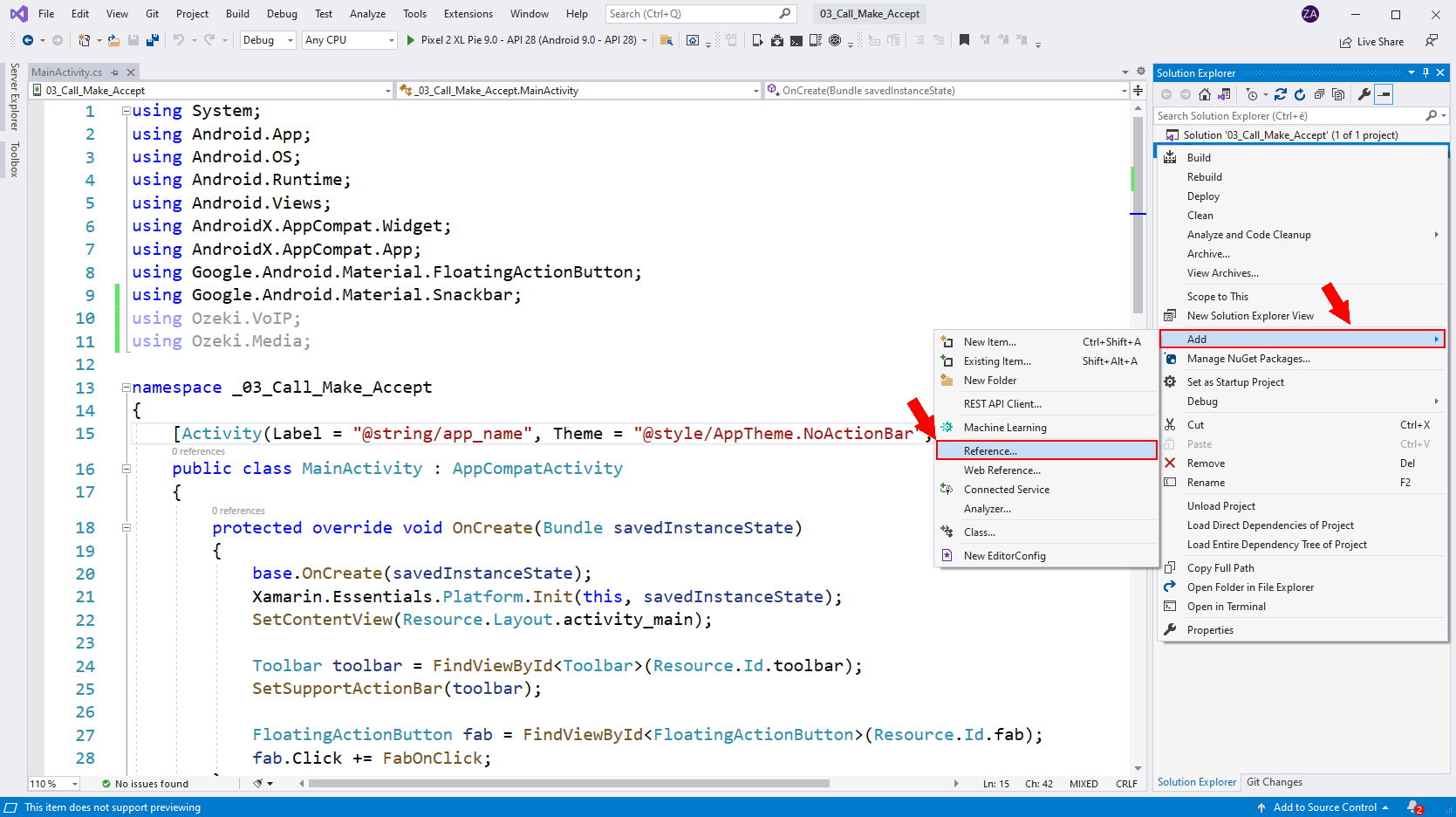
Browse for OzekiSDK.dll
In the reference manager window you are able to select and add references (Figure 2). Click on the Browse button to open the explorer and start browsing for the OzekiSDK.dll file on your disk.
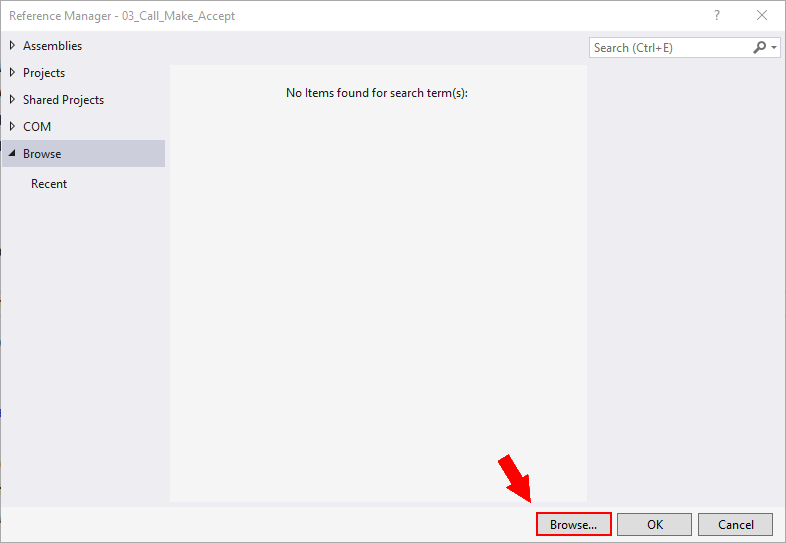
Add .dll file
Select the OzekiSDK.dll file (Figure 3). Click the Add button to add the .dll file as reference.
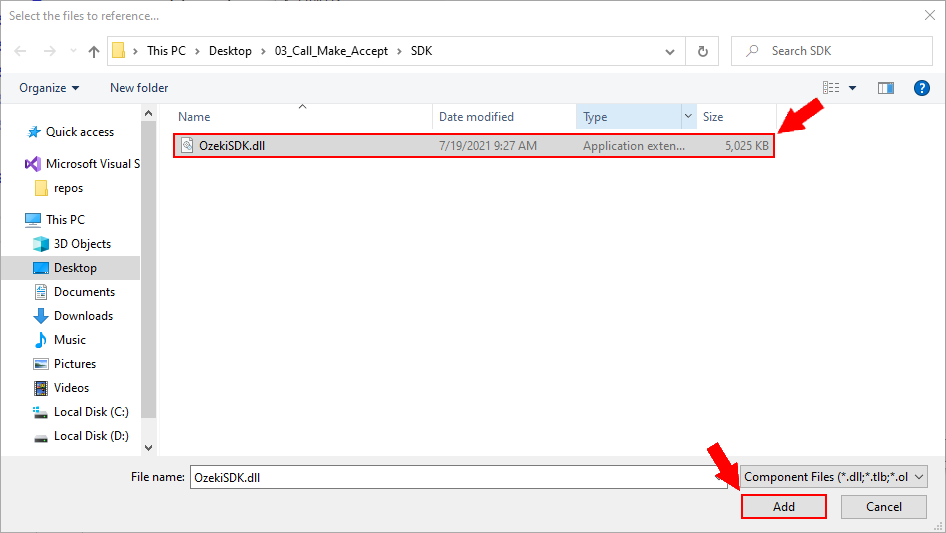
Import the components of the OzekiSDK.dll file
After you have added the reference, you can import the components of the OzekiSDK.dll file (Figure 4).
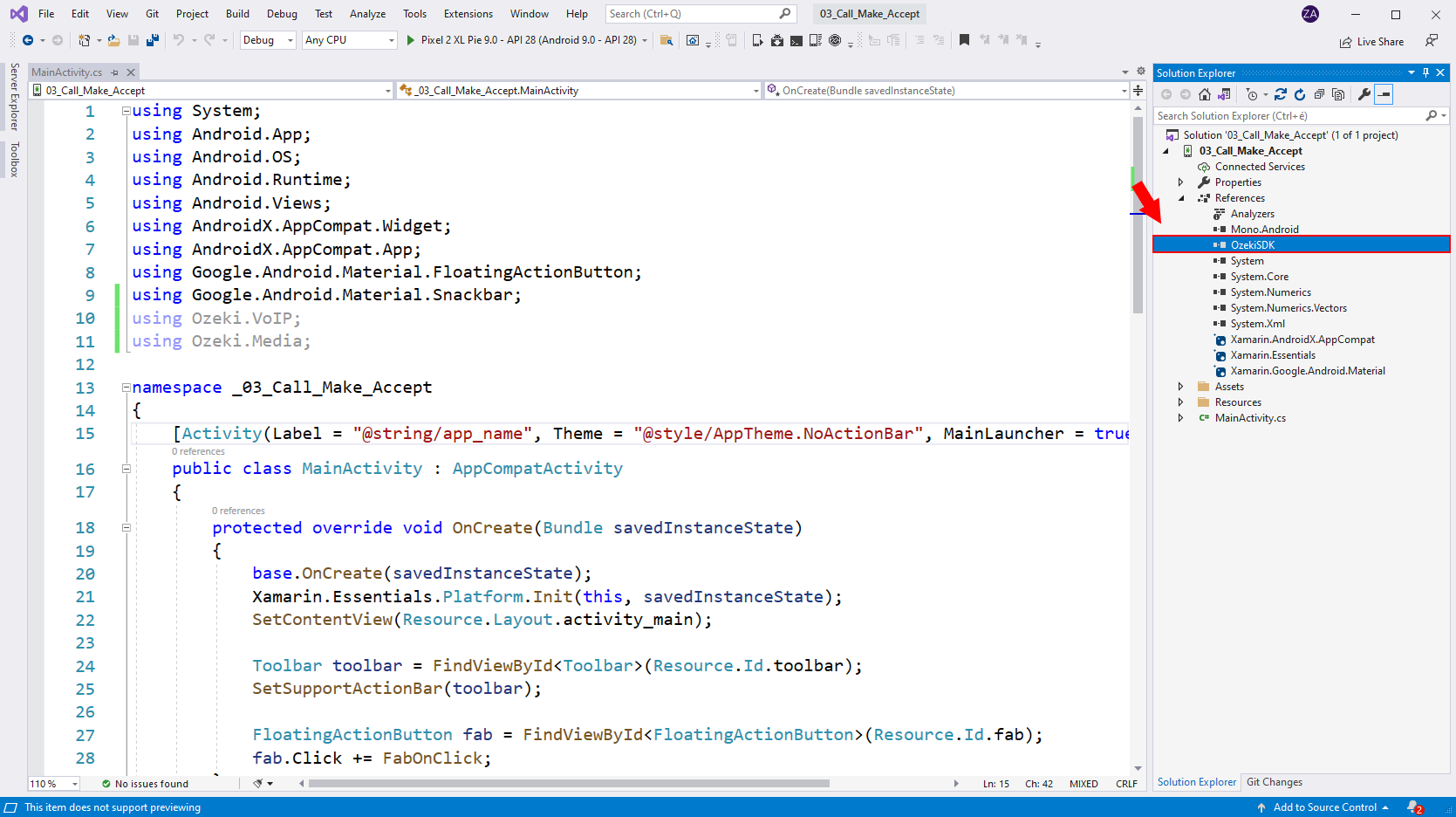
How to add a .dll reference in Visual Studio
In this quick video tutorial you will learn how to add a .dll reference in visual studio. This process is done in the Solution Explorer of Visual studio. You can right click to add reference, and then browse for your desired file. Follow along the steps in this video to add the OzekiSDK.dll file.
Creating the layout of the project
After we have added the .dll reference to our project, we can go forward by creating the layout of our application. To create the layout we will use a markup language called .xml. If you are familiar with HTML it is quite similar to that. When you design the template of the application, you have to add and id to each component you want to modify or use it's content in the future. For example if you want to add an on click function to a button you have to specify an id for that button because you will need that button to make a reference to the button.
You can copy and paste the source code into your project or you can download
the .xml files which are responsible for the layout of the application.
Download: layout.zip (1.87Kb)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="9"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="0"
android:text="SIP registration"
android:textSize="12pt"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputDisplayName"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="1"
android:hint="Display name"
android:inputType="text"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputUserName"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="2"
android:hint="Username"
android:inputType="text"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputAuthenticationID"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="3"
android:hint="Authentication ID"
android:inputType="text"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputRegisterPassword"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="4"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="Password"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputDomainHost"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="5"
android:hint="Host e.g.: 127.0.0.1"
android:inputType="text"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputDomainPort"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="6"
android:hint="Port e.g.: 5060"
android:inputType="text"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnLogin"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="7"
android:text="Login"
/>
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_row="8"
android:layout_column="0"
android:rowCount="2"
android:columnCount="1"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="10pt"
android:text="Log:"
android:layout_row="0"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/log"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="120dp"/>
</GridLayout>
</GridLayout>
</androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:rowCount="7"
android:columnCount="1"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/btnLogOut"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Logout"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="12pt"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="SIP registration"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/status"
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:text="Not registered"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/inputNumberToCall"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:layout_row="3"
android:textSize="18pt"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
/>
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_row="4"
android:layout_column="0"
android:rowCount="5"
android:columnCount="3"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnOne"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="1"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="0"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnTwo"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="1"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnThree"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="3"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="2"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnFour"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="4"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="0"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnFive"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="5"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="1"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSix"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="6"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="2"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSeven"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="7"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="0"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnEight"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="8"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="1"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnNine"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="9"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="2"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="*"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="0"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnZero"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="0"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="1"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnHashtag"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="#"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:layout_column="2"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
/>
</GridLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnInteractions"
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="5"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:backgroundTint="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:text="Dial"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/btnClear"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:layout_row="6"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="Clear"
/>
</GridLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
How to add the .xml files to the project
This short video tutorial will show you how to add the .xml files to the project. This process, again, is done in the Solution Explorer in Visual Studio. First you need to download the .xml files from this website. When the download is complete, you need to add these files into the layout folder of the example project. You can also open these files to view the layout in Visual Studio.
Creating the Softphone class
After the template is ready we can start writing some C# code to make the application functional. First of all we have to create a class called Softphone which will implement the ISoftphone interface. In the future we will use this softphone class to create a softphone object. The softphone object will be responsible for making the calls and receiving calls to and from other extensions that are registered in the Ozeki Phone System. In the following video I'll show you how to create the Softphone class.
using System;
using System.Threading;
using Ozeki.Media;
using Ozeki.VoIP;
using Ozeki.Common;
namespace _03_Call_Make_Accept
{
class Softphone
{
ISoftPhone _softphone; // softphone object
IPhoneLine _phoneLine; // phone line object
IPhoneCall _call; // the call object
Microphone _microphone;
Speaker _speaker;
MediaConnector _connector; // connects the devices to each other (eg. microphone, speaker, mediaSender, mediaReceiver)
PhoneCallAudioSender _mediaSender; // after connected with the microphone, this will be attached to the call
PhoneCallAudioReceiver _mediaReceiver; // after connected with the speaker, this will be attached to the call
private bool _incomingCall; // indicates wheter we have an incoming call (so, the phone is ringing)
#region Events
/// <summary>
/// Occurs when an incoming call received.
/// </summary>
public event EventHandler IncomingCall;
/// <summary>
/// Occurs when the registration state of the phone line has changed.
/// </summary>
public event EventHandler<RegistrationStateChangedArgs> PhoneLineStateChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Occurs when the state of the call has changed.
/// </summary>
public event EventHandler<CallStateChangedArgs> CallStateChanged;
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor, initalizes the softphone with deafult parameters.
/// </summary>
public Softphone()
{
_softphone = SoftPhoneFactory.CreateSoftPhone(5000, 10000);
_microphone = Microphone.GetDefaultDevice();
_speaker = Speaker.GetDefaultDevice();
_connector = new MediaConnector();
_mediaSender = new PhoneCallAudioSender();
_mediaReceiver = new PhoneCallAudioReceiver();
_incomingCall = false;
}
/// <summary>
/// Registers the SIP account to the PBX.
/// Calls cannot be made while the SIP account is not registered.
/// If the SIP account requires no registration, the RegisterPhoneLine() must be called too to register the SIP account to the ISoftPhone.
/// </summary>
public void Register(bool registrationRequired, string displayName, string userName, string authenticationId, string registerPassword, string domainHost, int domainPort)
{
try
{
// We need to handle the event, when we have an incoming call.
_softphone.IncomingCall += softphone_IncomingCall;
// To register to a PBX, we need to create a SIP account
var account = new SIPAccount(registrationRequired, displayName, userName, authenticationId, registerPassword, domainHost, domainPort);
// With the SIP account and the NAT configuration, we can create a phoneline.
_phoneLine = _softphone.CreatePhoneLine(account);
// The phoneline has states, we need to handle the event, when it is being changed.
_phoneLine.RegistrationStateChanged += phoneLine_PhoneLineStateChanged;
// If our phoneline is created, we can register that.
_softphone.RegisterPhoneLine(_phoneLine);
// For further information about the calling of the ConnectMedia(), please check the implementation of this method.
ConnectMedia();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error during SIP registration: " + ex);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// This will be called when the registration state of the phone line has changed.
/// </summary>
private void phoneLine_PhoneLineStateChanged(object sender, RegistrationStateChangedArgs e)
{
DispatchAsync(() =>
{
var handler = PhoneLineStateChanged;
if (handler != null)
handler(this, e);
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts the capturing and playing audio/video devices.
/// Other devices can be used (and started), for example: WebCamera or WaveStreamPlayback.
/// </summary>
private void StartDevices()
{
if (_microphone != null)
{
_microphone.Start();
}
if (_speaker != null)
{
_speaker.Start();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Stops the capturing and playing audio/video devices.
/// Other devices can be stopped, for example: WebCamera.
/// </summary>
private void StopDevices()
{
if (_microphone != null)
{
_microphone.Stop();
}
if (_speaker != null)
{
_speaker.Stop();
}
}
#region Media handling guide
/*
To send our voice through the microphone to the other client's speaker, we need to connect them.
We send our voice through the mediaSender, and we get the other client's voice through the mediaSender to our speaker object.
To disconnect these handlers, we will use the DisconnectMedia() method.
It is possible to use other mediahandlers with the connector, for example we can connect a WaveStreamPlayback or an MP3StreamPlayback object to the MediaSender, so we can play music/voice
during the call. For exmaple: when can create an IVR (Interactive Voice Response), we can create voice recorder etc.
For example:
We can connect an .mp3 file player (which plays an mp3 file into the voice call) by the "connector.Connect(Mp3StreamPlayback, mediaSender); " line.
(We should also create an MP3StreamPlayback object: "MP3StreamPlayback Mp3StreamPlayback; "
and we need to tell to this object the details (what to play into the speaker, etc.))
*/
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Connects the audio handling devices to each other.
/// The audio data will flow from the source to the destination.
/// </summary>
private void ConnectMedia()
{
if (_microphone != null)
{
_connector.Connect(_microphone, _mediaSender);
}
if (_speaker != null)
{
_connector.Connect(_mediaReceiver, _speaker);
}
}
private void DisconnectMedia()
{
if (_microphone != null)
{
_connector.Disconnect(_microphone, _mediaSender);
}
if (_speaker != null)
{
_connector.Disconnect(_mediaReceiver, _speaker);
}
}
private void WireUpCallEvents()
{
_call.CallStateChanged += (call_CallStateChanged);
}
private void WireDownCallEvents()
{
_call.CallStateChanged -= call_CallStateChanged;
}
private void softphone_IncomingCall(object sender, VoIPEventArgs<IPhoneCall> e)
{
_call = e.Item;
WireUpCallEvents();
_incomingCall = true;
DispatchAsync(() =>
{
var handler = IncomingCall;
if (handler != null)
handler(this, EventArgs.Empty);
});
}
private void call_CallStateChanged(object sender, CallStateChangedArgs e)
{
// the call has been answered
if (e.State == CallState.Answered)
{
StartDevices();
_mediaReceiver.AttachToCall(_call);
_mediaSender.AttachToCall(_call);
}
if (e.State == CallState.InCall)
{
StartDevices();
}
// the call has ended
if (e.State.IsCallEnded())
{
if (_call != null)
{
CallFinished();
}
}
DispatchAsync(() =>
{
var handler = CallStateChanged;
if (handler != null)
handler(this, e);
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts calling the specified number.
/// In this sample an outgoing call can be made if there is no current call (outgoing or incoming) on the phone line.
/// </summary>
public void StartCall(string numberToDial)
{
if (_call == null)
{
_call = _softphone.CreateCallObject(_phoneLine, numberToDial);
WireUpCallEvents();
// To make a call simply call the Start() method of the call object.
_call.Start();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Answers the current incoming call.
/// </summary>
public void AcceptCall()
{
// when the value of the incomingCall member is true, there is an incoming call
if (_incomingCall)
{
_incomingCall = false;
_call.Answer();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Hangs up the current call.
/// </summary>
public void HangUp()
{
if (_call != null)
{
_call.HangUp();
_call = null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// If the call ends, we won't need our speaker and microphone anymore to communicate,
/// until we enter into a call again, so we are calling the StopDevices() method.
/// The mediaHandlers are getting detached from the call object
/// (since we are not using our microphone and speaker, we have no media to send).
/// We won't need the call's events anymore, becouse our call is about to be ended,
/// and with setting the call to null, we are ending it.
/// </summary>
public void CallFinished()
{
StopDevices();
_mediaReceiver.Detach();
_mediaSender.Detach();
WireDownCallEvents();
_call = null;
}
/// <summary>
/// This method is used to solve the task blockings.
/// </summary>
private void DispatchAsync(Action action)
{
var task = new WaitCallback(o => action.Invoke());
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(task);
}
}
}
A part of the code above may be familiar from SIP registration example. Creating the MainActivity.cs activity
After the softphone class is ready we have to create a form that collect all the data that is needed for the SIP registration. To use the credentials in the whole application, we will save them as a preference what is provided by the Xammarin. In the following video I'll show you how to make create the MainActivity.cs file.
How to create the MainActivity.cs file
This video tutorial demonstrates how to create the MainActivity.cs file. This is done by modifying the example code in Visual Studio. Follow along the steps peresented in this video and write the corresponding pieces of code to create this file.
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.OS;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using AndroidX.AppCompat.App;
using Android.Widget;
namespace _03_Call_Make_Accept
{
[Activity(Label = "@string/app_name", Theme = "@style/AppTheme.NoActionBar", MainLauncher = true)]
public class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity
{
Button _btnLogin;
TextView _log;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.Init(this, savedInstanceState);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_main);
TestIfUserLoggedIn();
_btnLogin = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnLogin);
_btnLogin.Click += OnClick__btnLogin;
_log = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.log);
}
private void OnClick__btnLogin(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string displayName = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputDisplayName).Text;
string userName = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputUserName).Text;
string authentiactionID = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputAuthenticationID).Text;
string registerPassword = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputRegisterPassword).Text;
string domainHost = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputDomainHost).Text;
int domainPort = -1;
try
{
domainPort = Int32.Parse(FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputDomainPort).Text);
}
catch (Exception error)
{
_log.Text += "Please provide a valid port number!\n";
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(displayName) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(userName)
&& !string.IsNullOrEmpty(authentiactionID) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(registerPassword)
&& !string.IsNullOrEmpty(domainHost) && domainPort != -1)
{
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("display_name", displayName);
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("user_name", userName);
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("authentication_id", authentiactionID);
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("register_password", registerPassword);
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("domain_host", domainHost);
Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Set("domain_port", domainPort);
StartActivity(typeof(DialingActivity));
}
else
{
_log.Text += "Please fill all the required fields!\n";
}
}
private void TestIfUserLoggedIn()
{
if (Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.ContainsKey("display_name"))
{
StartActivity(typeof(DialingActivity));
}
}
public override bool OnCreateOptionsMenu(IMenu menu)
{
MenuInflater.Inflate(Resource.Menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
public override bool OnOptionsItemSelected(IMenuItem item)
{
int id = item.ItemId;
if (id == Resource.Id.action_settings)
{
return true;
}
return base.OnOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
public override void OnRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, string[] permissions, [GeneratedEnum] Android.Content.PM.Permission[] grantResults)
{
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.OnRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
base.OnRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
}
}
}
Creating the MainActivity.cs activity
After the form is ready we can go forward by creating the softphone. To do that we have to add a new activity to the project and name it DialingActivity.cs.
using Android.App;
using Android.OS;
using Ozeki.VoIP;
using System;
using Android.Widget;
namespace _03_Call_Make_Accept
{
[Activity(Label = "DialingActivity")]
public class DialingActivity : Activity
{
private static Softphone _mySoftphone;
Button _btnInteractions;
TextView _btnLogOut;
TextView _btnClear;
Button _btnZero;
Button _btnOne;
Button _btnTwo;
Button _btnThree;
Button _btnFour;
Button _btnFive;
Button _btnSix;
Button _btnSeven;
Button _btnEight;
Button _btnNine;
Button _btnStar;
Button _btnHashtag;
TextView _inputNumberToCall;
TextView _status;
CallState _callState;
bool _incomingCall;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.Init(this, savedInstanceState);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_dialing);
InitSoftphone();
Register();
_incomingCall = false;
_btnInteractions = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnInteractions);
_btnInteractions.Click += OnClick__btnInteractions;
_btnLogOut = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.btnLogOut);
_btnLogOut.Click += delegate { Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Clear(); StartActivity(typeof(MainActivity)); };
_btnClear = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.btnClear);
_btnClear.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text = ""; };
_btnZero = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnZero);
_btnZero.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "0"; };
_btnOne = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnOne);
_btnOne.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "1"; };
_btnTwo = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnTwo);
_btnTwo.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "2"; };
_btnThree = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnThree);
_btnThree.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "3"; };
_btnFour = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnFour);
_btnFour.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "4"; };
_btnFive = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnFive);
_btnFive.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "5"; };
_btnSix = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnSix);
_btnSix.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "6"; };
_btnSeven = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnSeven);
_btnSeven.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "7"; };
_btnEight = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnEight);
_btnEight.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "8"; };
_btnNine = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnNine);
_btnNine.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "9"; };
_btnStar = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnStar);
_btnStar.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "*"; };
_btnHashtag = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnHashtag);
_btnHashtag.Click += delegate { _inputNumberToCall.Text += "#"; };
_inputNumberToCall = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.inputNumberToCall);
_status = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.status);
}
// Initializes a softphone object
private void InitSoftphone()
{
_mySoftphone = new Softphone();
_mySoftphone.PhoneLineStateChanged += mySoftphone_PhoneLineStateChanged;
_mySoftphone.CallStateChanged += mySoftphone_CallStateChanged;
_mySoftphone.IncomingCall += mySoftphone_IncomingCall;
}
/*
This function makes the interactions button to execute different tasks
based on the actual CallState of the phone
*/
private void OnClick__btnInteractions(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_callState == CallState.Ringing && _incomingCall)
{
_mySoftphone.AcceptCall();
_incomingCall = false;
}
else if (_callState == CallState.Answered || _callState == CallState.InCall)
{
_mySoftphone.HangUp();
}
else
{
string currentNumber = _inputNumberToCall.Text;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(currentNumber))
{
_mySoftphone.StartCall(currentNumber);
}
}
}
// When the phone line state changes this function will be called
private void mySoftphone_PhoneLineStateChanged(object sender, RegistrationStateChangedArgs e)
{
if (e.State == RegState.Error || e.State == RegState.NotRegistered)
{
_status.Text = "Not registered.";
Register();
}
else if (e.State == RegState.RegistrationSucceeded)
{
_status.Text = "Registered.";
}
}
// When there is an incoming call this function will be called
private void mySoftphone_IncomingCall(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
_incomingCall = true;
}
// When the CallState changes this function will be called
private void mySoftphone_CallStateChanged(object sender, CallStateChangedArgs e)
{
_callState = e.State;
Console.WriteLine(e.State);
if (_callState == CallState.Ringing && _incomingCall)
{
_btnInteractions.Text = "Answer";
}
else if (_callState == CallState.Answered || _callState == CallState.InCall
|| _callState == CallState.Setup || _callState == CallState.Ringing &&
!_incomingCall)
{
_btnInteractions.Text = "Hang up";
}
else
{
_btnInteractions.Text = "Dial";
}
}
// SIP registration with the stored session data
private void Register()
{
bool registrationRequired = true;
string displayName = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("display_name", "");
string userName = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("user_name", "");
string authenticationID = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("authentication_id", "");
string registerPassword = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("register_password", "");
string domainHost = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("domain_host", "");
int domainPort = Xamarin.Essentials.Preferences.Get("domain_port", 5060);
_mySoftphone.Register(registrationRequired, displayName, userName, authenticationID, registerPassword,
domainHost, domainPort);
}
// To prevent the user from exiting the session on
// the click of the back button
public override void OnBackPressed()
{
return;
}
}
}
How to createthe DialingActivity.cs file
This video tutorial demonstrates how to create the DialingActivity.cs file. Similarly to MainActivity.cs, this is done by modifying the example code in Visual Studio. Follow along the steps peresented in this video and write the corresponding pieces of code to create this file.
How to ask for microphone permission
If you want to build a sopftphone application, you will need to ask for microphone permission for your application. In the following video I'll show you, how to allow the microphone in your Xamarin Android application.
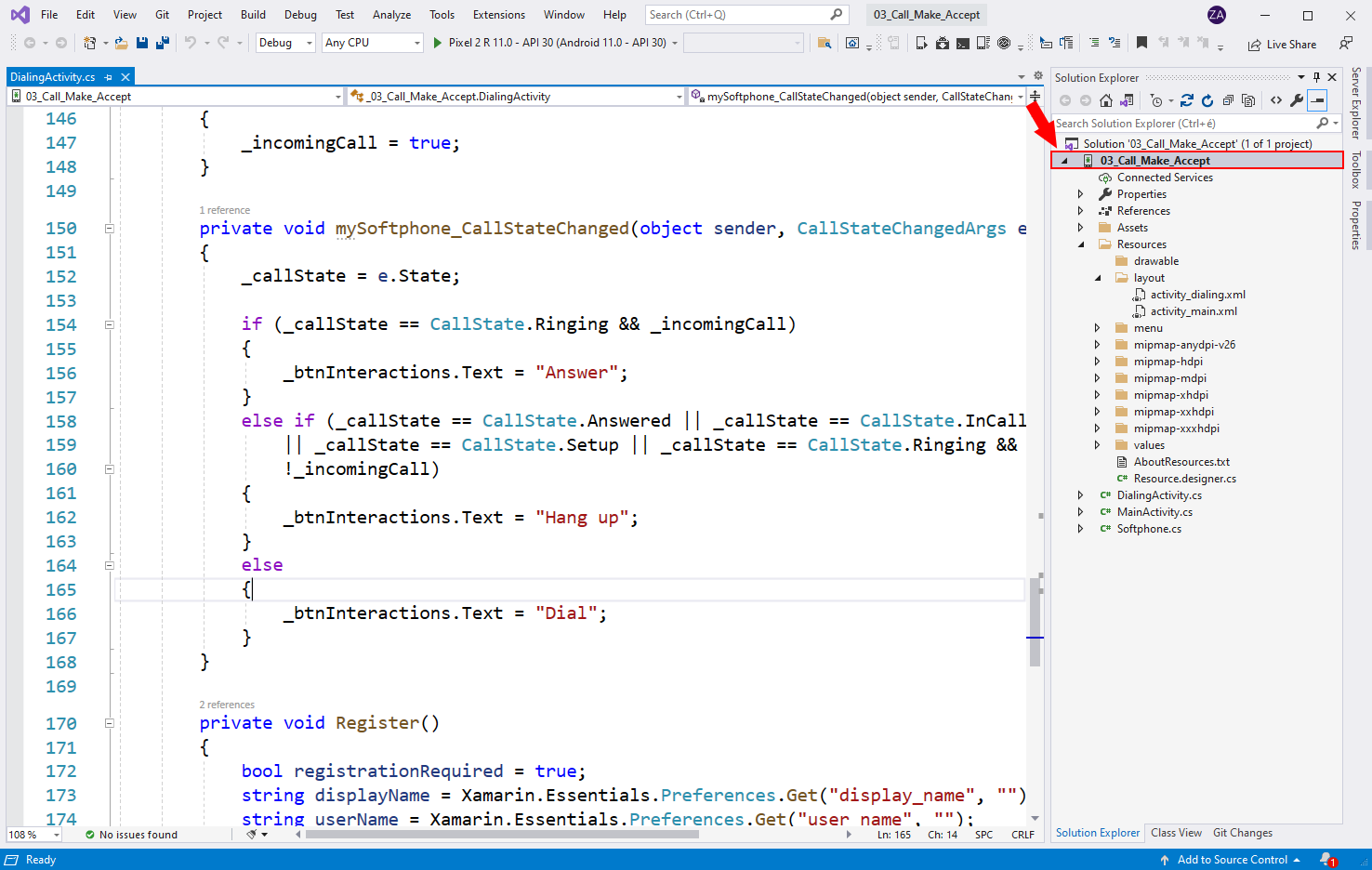
Select the Android Manifest tab
Right click on 03_Call_Make_Accept on the right (Figure 6). Click on Properties on the very bottom.
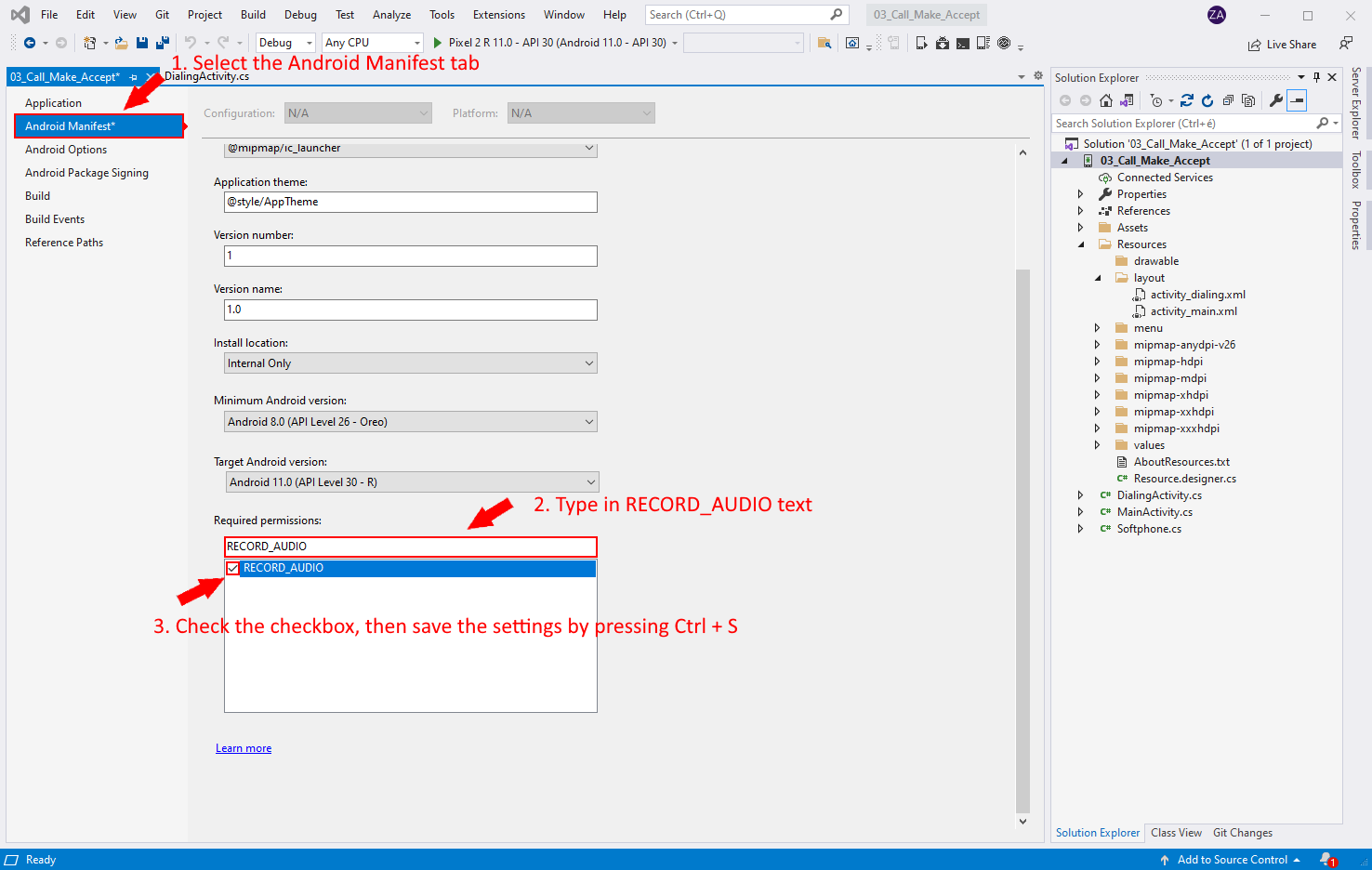
Search for the RECORD_AUDIO option
The next step is to search for the RECORD_AUDIO option in the properties (Figure 7). First you need to select the Android Manifest tab by clicking on it. Next, under "Required permissions" type in "RECORD_AUDIO". Finally, check the checkbox next to "RECORD_AUDIO". Press Ctrl+s to save these settings.
Running the Softphone application
After the softphone is ready we can start debugging the application on an Android device with a version that's higher than Android 8.0. If we don't have an android device we can create an android emulator in the Visual Studio Community. In the following video you will also see, how to allow microphone for your application.
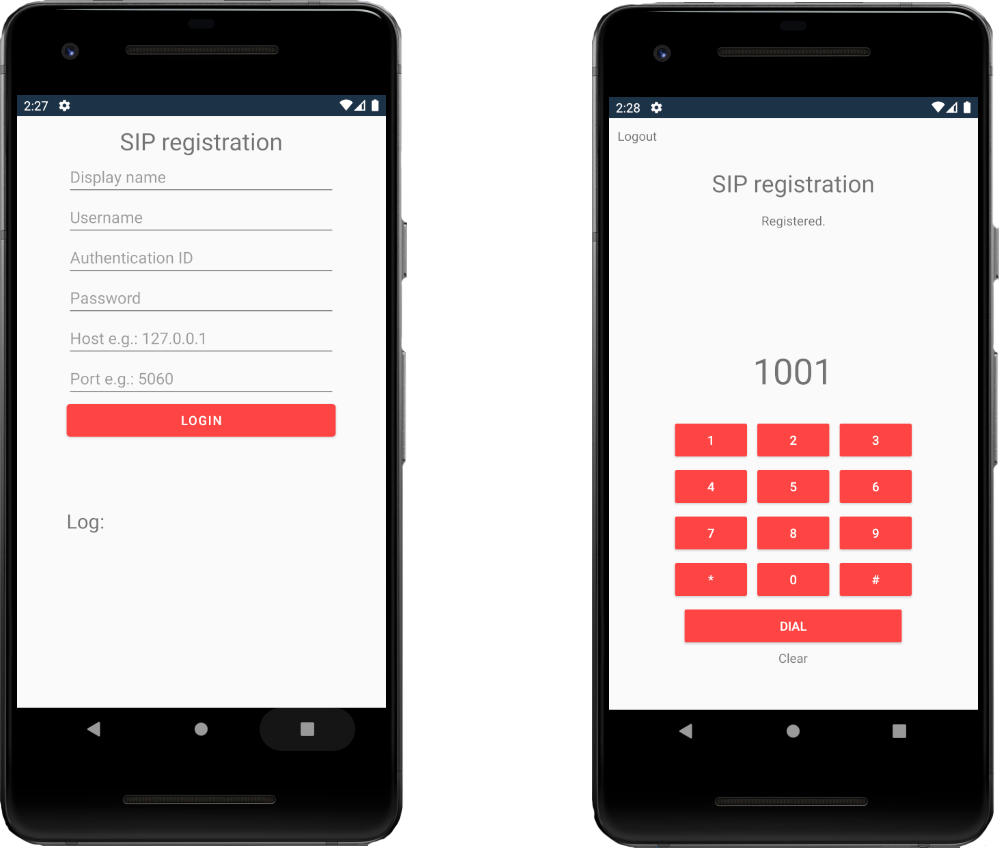
Example application to make and accept calls
This image shows an example application that can make and accept calls (Figure 9).
Summary
We did our very best to make it simple and to walk you through all the details as painlessly as possible. If you have followed the directions closely, you should be able to make calls using the Android softphone Now that you know how to make and receive calls with the Ozeki VoIP SIP SDK, you can continue your journey by learning the process of controlling the call or you can explore the SIP Instanct Messaging of the SDK.
